Figure 5.
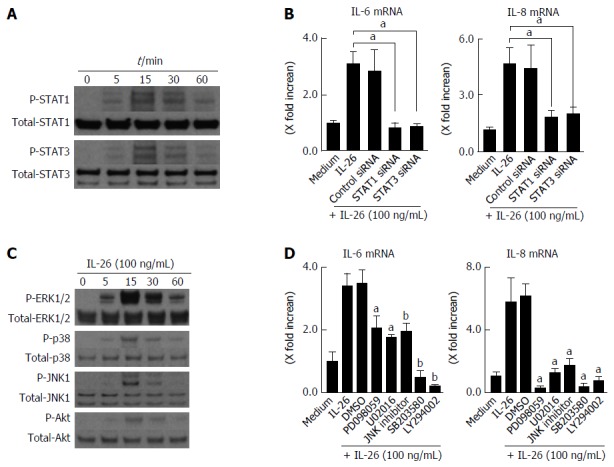
Involvement of STAT1, STAT3, MAPKs and PI3K/Akt activation in interleukin-26-stimulated interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 induction. A: STAT1 and STAT3 activation in response to IL-26. Human colonic SEMFs were stimulated with 100 ng/mL of IL-26 for the indicated pre-determined times, and the phosphorylation (P-) of STAT1 and STAT3 was evaluated by immunoblot analyses. The data are representative of two independent experiments; B: The effects of siRNAs for STAT1 and STAT3 on IL-26-induced mRNA expression of IL-6 and IL-8. Cells were transfected with siRNA for STAT1 and STAT3 or control siRNA, and were incubated for 3 h with or without 100 ng/mL of IL-26. The mRNA expression of IL-6 and IL-8 was then evaluated using real-time PCR. The mRNA expression of IL-6 and IL-8 was converted to a value relative to β-actin mRNA expression and presented as fold-increase relative to the results for medium alone (no stimulation); C: MAPKs and PI3K/Akt activation in response to IL-26. Human colonic SEMFs were stimulated with 100 ng/mL of IL-26 for the indicated pre-determined times, and the phosphorylation (P-) of MAPKs and PI3K was evaluated by immunoblot analyses. The data are representative of two independent experiments; D: Effects of inhibitors of MAPKs and PI3K/Akt on IL-6 and IL-8 induction by IL-26 in human colonic SEMFs. The cells were pretreated with 10 μmol/L of a p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580) or an MEK1/2 inhibitor (U0216 or PD098059), or with 3 μmol/L of a JNK inhibitor (JNK inhibitor I) or 25 μmol/L of a PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) for 30 min, and were then incubated with or without 100 ng/mL of IL-26 for 3 h. The mRNA expression of IL-6 and IL-8 was converted to a value relative to β-actin mRNA expression and presented as fold-increase relative to the results for medium alone. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of four independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs IL-26 stimulation. IL: Interleukin; SEMFs: Subepithelial myofibroblasts.
