Fig. 4.
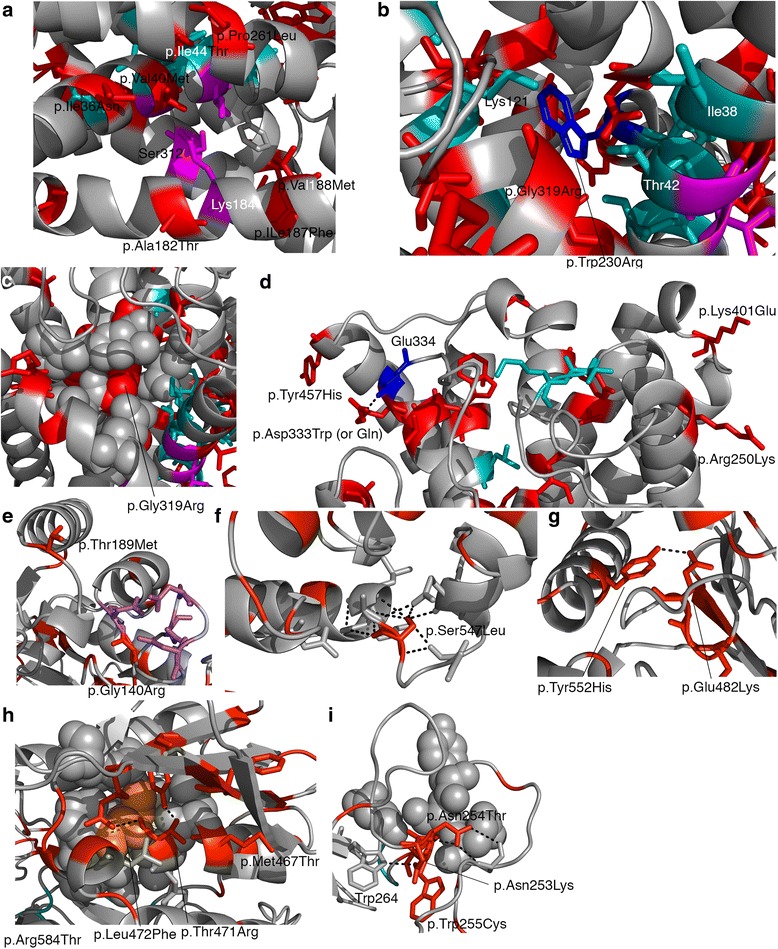
Mutations in b(0+)AT and rBAT. In all images the mutated residues are displayed as red sticks in their wild type format. Predicted functional residues are coloured cyan. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed black lines. Images a-d refer to b(0+)AT and images E-I refer to rBAT. a p.Ile187Phe and p.Ala182Thr mutations are adjacent to p.Lys184 which is thought to play a role equivalent to sodium in sodium dependent transporters. b p.Trp230Arg (coloured blue) is adjacent to multiple functional residues. c The mutation p.Gly319Arg occurs in a buried region (p.Gly319 shown in red spheres). d. Mutations close to the end of transmembrane helices may reduce stability in the membrane. e mutations occurring close to the predicted calcium binding site in rBAT. f mutation p.Ser547Leu will remove hydrogen bonding. g p.Tyr552His and p.Glu482Lys as wild type form a hydrogen bond, it is not clear if this will be retained upon mutation. h multiple mutations present in a single region. p.Leu472Phe (orange spheres) will result in increased size in well packed area. Other mutations will remove hydrogen bonding. I) Mutations occur in residues 253–256
