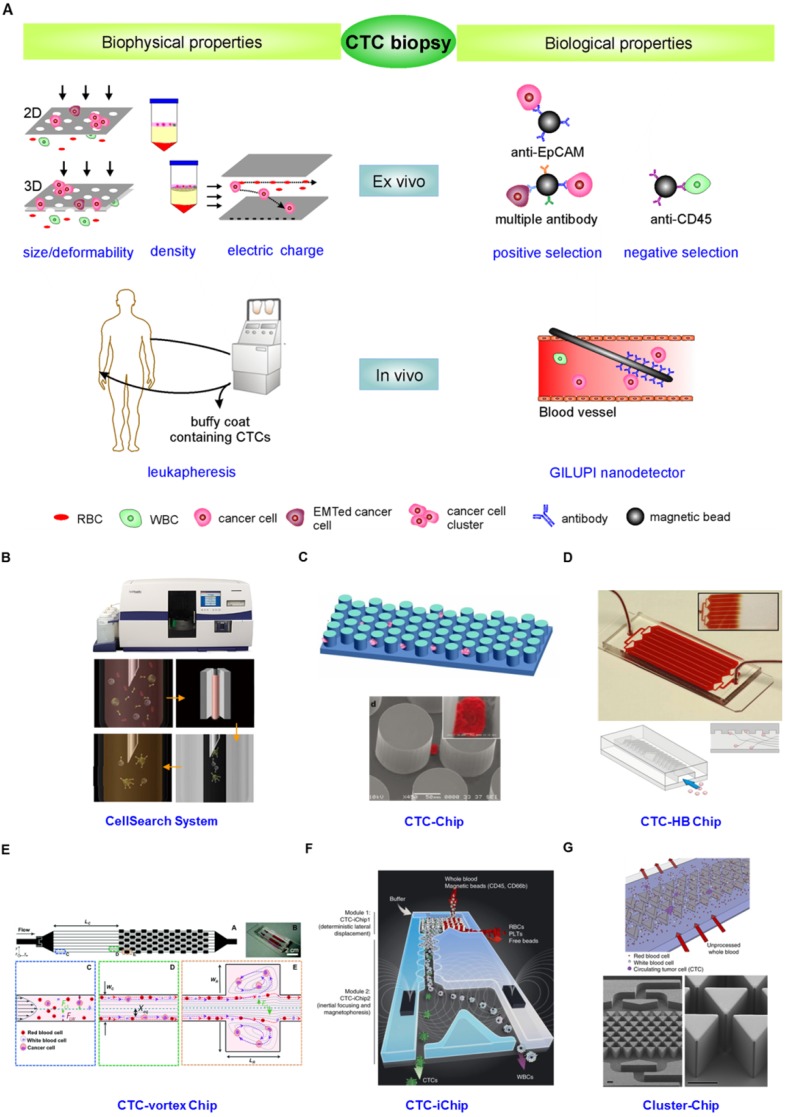
Figure 4.
(A) CTC enrichment methodologies can be summarized into physical and biological property-dependent methodologies. Physical property-dependent methodologies include size-, density-, and electrical charge-based strategies. Among the biological property-dependent methodologies, the EpCAM antibody is commonly used for positive selection. Multiple antibodies for positive selection as well as CD-45-mediated negative depletion have been introduced to eliminate loss of CTC subpopulations. Leukapheresis and GLUPI nanodetection enable the enrichment of CTCs in vivo. Devices developed to improve the enrichment efficiency include (B) the CellSearch system; (C) the CTC-Chip, the first microfluidic chip integrated into CTC enrichment; (D) the CTC-HB chip, in which a herringbone design enables passive mixing, increasing interactions between CTCs and an antibody-coated channel surface; (E) the CTC-vortex Chip, which combines the use of micro-scale vortices and inertial focusing; (F) the CTC-iChip, capable of either positive or negative selection of CTCs; (G) the Cluster-Chip, capable of isolating CTC clusters through specialized bifurcating traps. B-G were reprinted with permission from ref 155, 12, 108, 91, 74, 75, respectively.