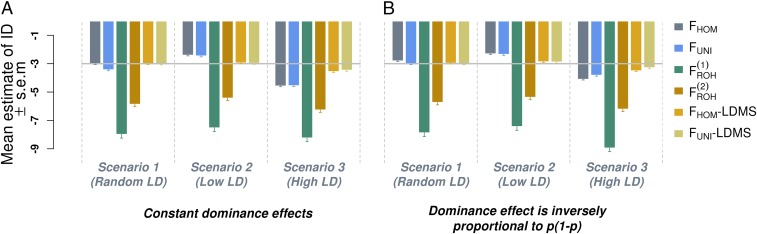
Fig. 1.
Averaged estimates of inbreeding depression (ID) from 1,000 simulated datasets. Datasets were simulated assuming a true ID parameter b = −3 (horizontal gray line) phenotypic SD for complete inbreeding. In scenario 1 the causal variants were randomly sampled from all observed SNPs, whereas in scenarios 2 and 3 they were respectively sampled from low- and high-LD regions of the genome. In A the expectation of the dominance effects ( for the jth causal variant) is constant (neutral model) whereas in panel B is inversely proportional to the variance of the minor allele count at each causal variant. , excess homozygosity inbreeding measure; , runs of homozygosity-based inbreeding measures; , measure of inbreeding based on correlation between uniting gametes; LDMS, LD and minor allele frequency stratified inference; SEM, SE of the mean.