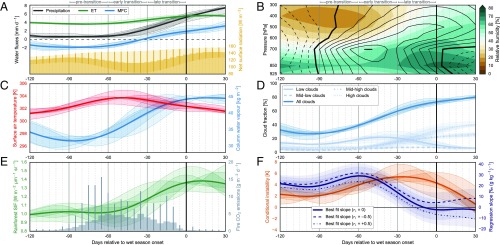
Fig. 2.
Onset-relative low-pass filtered composites of area mean precipitation from Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM), ET and MFC from ERA-Interim, and net absorbed surface radiation from Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Synoptic Radiative Fluxes and Clouds (SYN1Deg) (A); vertical distributions of RH (shading) and time rates of change in equivalent potential temperature (; contour interval 0.02 K d−1) computed from Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) observations (B); surface air temperature and column water vapor (CWV) from AIRS (C); low (<700 hPa; 3 km above sea level), midlow (700–500 hPa; 3–5.5 km), midhigh (500–300 hPa; 5.5–10 km), high (>300 hPa; 10 km), and total cloud cover from CERES SYN1deg (D); solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) for rainforests from the Global Ozone Monitoring Instrument 2 and fire emissions of CO2 from Version 3.1 of the Global Fire Emissions Database (E); conditional instability in the lower–middle troposphere () based on AIRS and best-fit linear slopes of D against specific humidity () in the free troposphere based on TES (F). Shaded areas in A and C–F and error bars in A and E illustrate estimated uncertainties. Data sources, quality control criteria, and uncertainty calculations are provided in SI Text.