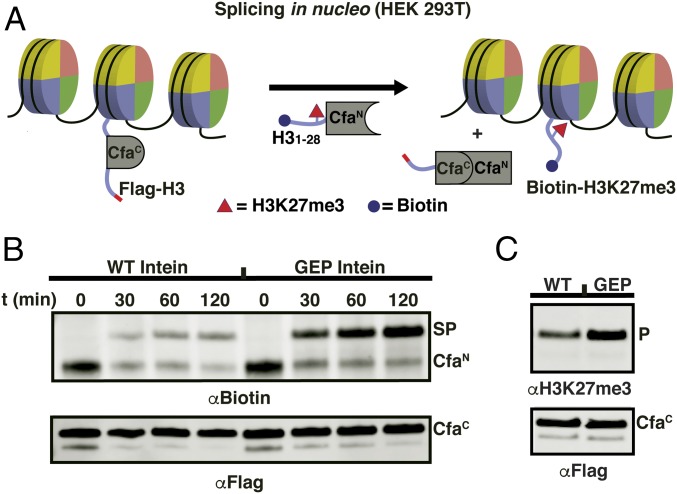
Fig. 5.
In nucleo semisynthesis of chromatin with the CfaGEP split intein. (A) Schematic of in nucleo protein splicing on histone H3 in chromatin. Nucleosomes are depicted as discs. Extracted nuclei from mammalian cells containing transfected Flag-H31–28-CfaC-H329–135 (WT or GEP loop sequence) are treated with semisynthetic Biotin-H31–28K27me3-CfaN (spliced product = Biotin-H3K27me3). (B) Western blot analysis of in nucleo splicing reactions on histone H3 as depicted in A. PTS reactions were quenched at the indicated times with 80 mM iodoacetamide. (Top) αBiotin analysis of in nucleo splicing. CfaN, starting material (Biotin-H31–28K27me3-CfaN); SP, spliced product (Biotin-H3K27me3). (Bottom) αFlag Western blot analysis of in nucleo splicing reactions. CfaC, starting material (Flag-H31–28-CfaC-H329–135). In the case of the CfaGEP intein, the majority of CfaN starting material is converted to SP. For the CfaWT intein, in contrast, competing thiolysis (SI Appendix, Fig. S10) of the CfaN dominates, resulting in a loss of biotin signal. (C) Western blot analysis comparing in nucleo splicing yield of the CfaWT (WT) and CfaGEP (GEP) inteins (2 h, 37 °C). (Top) αH3K27me3 Western blot analysis. P, H3K27me3. (Bottom) αFlag Western blot analysis. CfaC, Flag-H31–28-CfaC-H329–135.