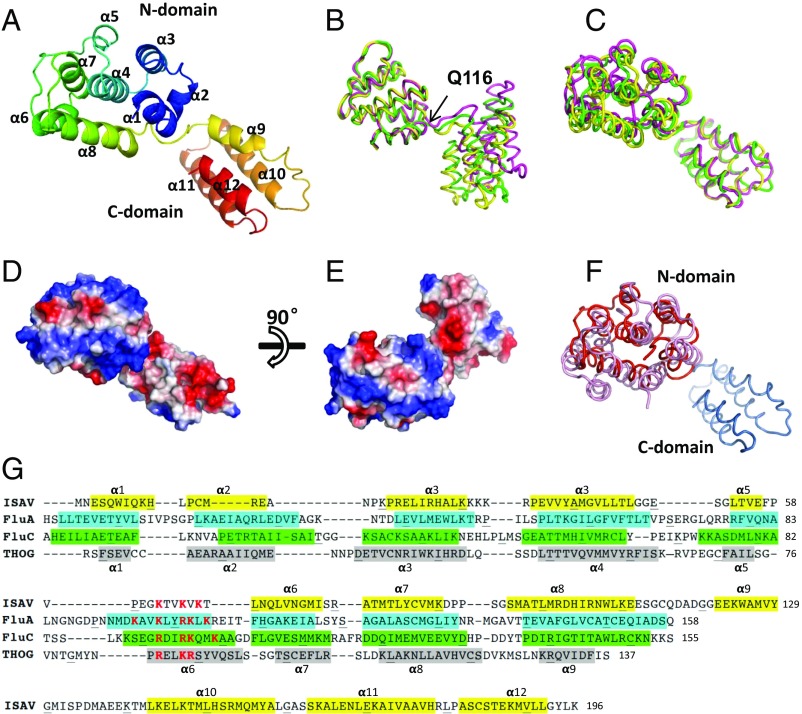
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of the ISAV-M1. (A) ISAV-M1 crystal structure. The ribbon diagram is rainbow colored with the N terminus in blue and C terminus in red. (B) Superimposition of the three ISAV-M1 molecules related by pseudotranslation symmetry. The three molecules A–C are shown in green, magenta, and yellow, respectively. Superimposition was calculated based on the N domain. Q116 is the hinge point where the structural deviation of the C domain begins. (C) Superimposition of the three ISAV-M1 molecules based on the C domain. (D and E) Molecular surface of ISAV-M1 colored by electrostatic potential viewed from different directions. (F) ISAV-M1 superimposed onto FLUA-M1. ISAV-M1 is shown in red with FLUA-M1 shown in pink. (G) Secondary structure assignment of M1 proteins from ISAV, FluA (influenza A virus), FluC (influenza C virus), and THOG (thogotovirus). The four sequences are aligned according to structure alignment by DALI combined with some manual adjustment. Residues forming α-helices are colored (i.e., ISAV in yellow, FluA in cyan, FluC in green, and THOG in gray) and numbered. The α-helix labels on Top of the aligned sequences apply to ISAV, and the α-helix labels at the Bottom of the aligned sequences apply to FluA. For FLUA-M1, FLUC-M1, and THOG-M1, only the N-domain sequences are shown as the structures of their C domains are not yet available.