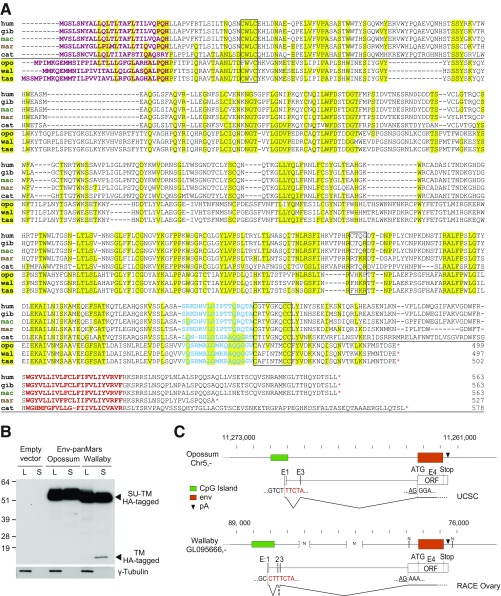
Fig. S4.
Characterization of the marsupial env-panMars gene and protein. (A) Amino acid sequence homology between marsupial env-panMars (coordinates as in ref. 12) and HEMO proteins from representative simian species and domestic cat (Table S5). Every amino acid of a marsupial sequence that is found at the same position in a simian or cat sequence is highlight in yellow. Same color code for the characteristic env domains as in Fig. 1C. cat, cat; gib, gibbon; hum, human; mac, macaque; mar, marmoset; opo, opossum; tas, Tasmanian devil; wal, wallaby. *Stop codon. (B) Detection of the HA-tagged opossum and wallaby env-panMars proteins. Western blot of cell lysates (L) and supernatants (S) from 293T cells transfected with the phCMV-empty, phCMV-Opossum-env, or phCMV-Wallaby-env expression vectors. Detection with an anti-HA antibody (Upper) and an anti–γ-tubulin antibody (Lower). (C) Structure of the env-panMars gene locus and transcripts for the opossum (Upper) and wallaby (Lower). Schematic representation of the env-panMars locus, with the env-ORF in orange and the CpG island in green. N represents uncharacterized sequences. Black arrowheads (pA) position the AATAAA polyadenylation signal sequence. Intron–exon structures are from UCSC for the opossum and were characterized by RACE PCR experiments for the wallaby (RNA from the ovaries; SI Methods). Nucleotide sequences of the start site (TTCTA for the opossum and CTTTCTA for the wallaby) and the env ORF acceptor splice site are indicated, with the dinucleotide AG (end of intron) underlined; E2-E3 intron is dotted to indicate E3 skipping in a fraction of the wallaby transcripts, as observed for the HEMO gene.