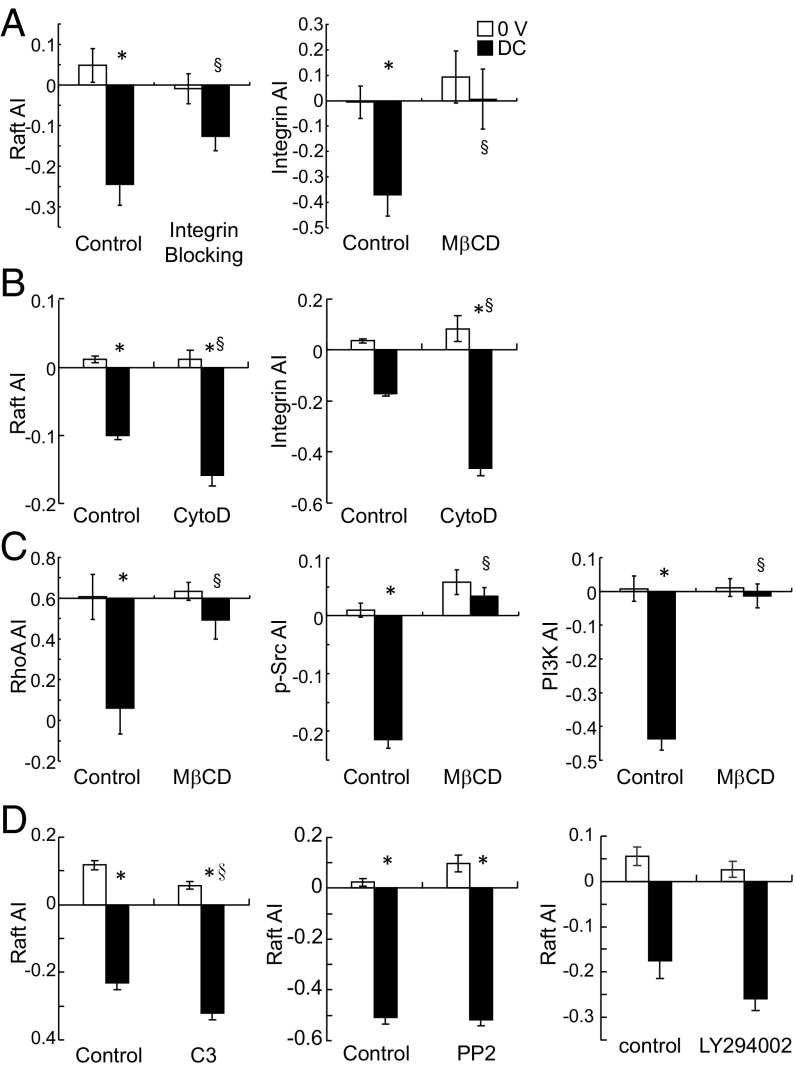
Fig. 3.
Lipid rafts act upstream of intracellular structure and signaling mechanisms. (A) Integrin blocking partially suppressed lipid raft polarization in response to applied EF, whereas lipid raft disruption diminished integrin polarization in EF (n = 32–58, *P < 0.005 vs. 0 V, §P < 0.05 vs. control). (B) Actin cytoskeleton disruption enhanced polarized lipid raft and integrin distribution in EF (n = 20–262, *P < 0.0001 vs. 0 V, §P < 0.0001 vs. control). (C) Lipid raft disruption attenuated polarized RhoA, Src, and PI3K distribution (n = 4–73, *P < 0.01 vs. 0 V, §P < 0.02 vs. control), whereas (D) RhoA, Src, or PI3K inhibition (with C3 exoenzyme, PP2, and LY294002, respectively) did not suppress lipid raft redistribution (n = 70–127, *P < 0.0001 vs. 0 V, §P < 0.001 vs. control).