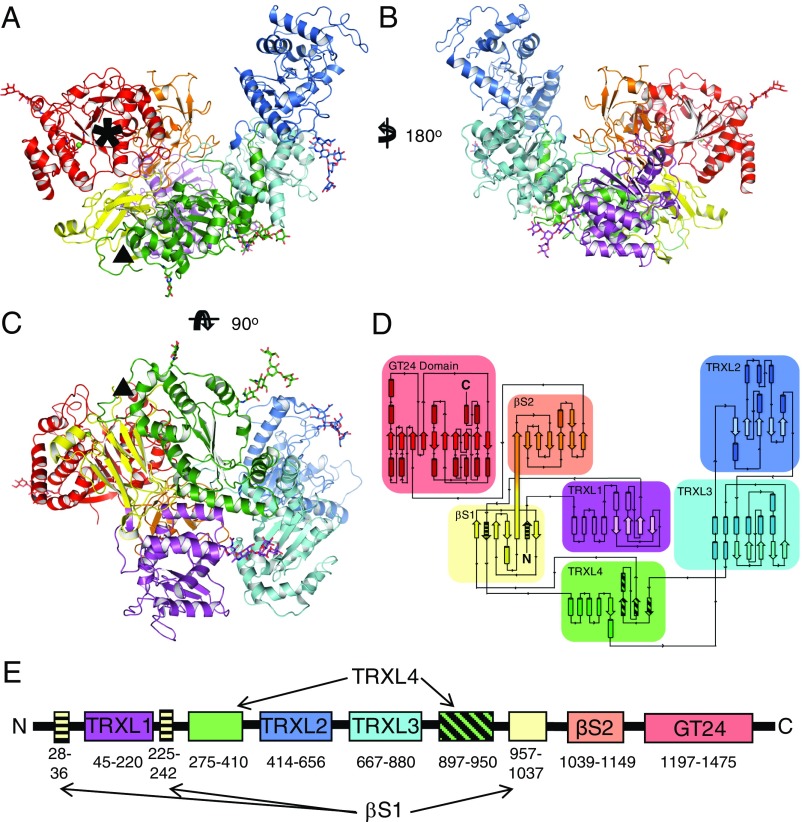
Fig. 1.
Structure and topology of CtUGGT. (A–C) Three orthogonal views of the 3.5-Å crystal structure of the CtUGGT P61 (intermediate) form. The structure spans residues 27–1,473, except for disordered loops 243–285 and 1,334–1,340, and the residue gap 1,153–1,195 around the endoproteolysis site, also disordered in the crystal. The seven domains are in cartoon representation: TRXL1 (purple), TRXL2 (blue), TRXL3 (cyan), TRXL4 (green), βS1 (yellow), βS2 (orange), and GT (red). The five N-linked glycans (at N56, N329, N638, N894, and N1227) are in stick representation. Six conserved cysteine residues form three disulfide bonds, one in the TRXL1 domain (CtUGGT C138–C150) and two in the GT domain (CtUGGT C1330–C1423 and C1419–C1437). The Ca2+ ion bound at the conserved nucleotide-sugar coordinating 1302DAD1304 motif is represented as a green sphere. A black asterisk marks the catalytic site. A black triangle marks the dangling ends around the disordered loop (CtUGGT residues 243–285, between the second strand of the βS1 sandwich and the N-terminal part of the TRXL4 domain) corresponding to the region to which Sep15 binding has been mapped in D. melanogaster UGGT (37). (D and E) The 2- and 1-dimensional topological diagrams of CtUGGT, respectively. The first and second strands of β-sandwich βS1 (residues 28–36 and 225–242, respectively, striped yellow) flank the part of sequence encoding TRXL1 (residues 45–220, magenta), with the rest of βS1 encoded by a portion of sequence (residues 957–1,037, yellow) more than 700 residues downstream of the sandwich’s second strand. TRXL1 adopts a noncanonical subdomain structure, different from all structures of Pfam family PF01323 members, in which an N-terminal α-helical subdomain is followed by a C-terminal thioredoxin subdomain. The N- and C-terminal halves of TRXL4 (residues 275–410 and 897–950, the latter portion in striped green) occur in the standard order but are separated in sequence by TRXL2 and TRXL3.