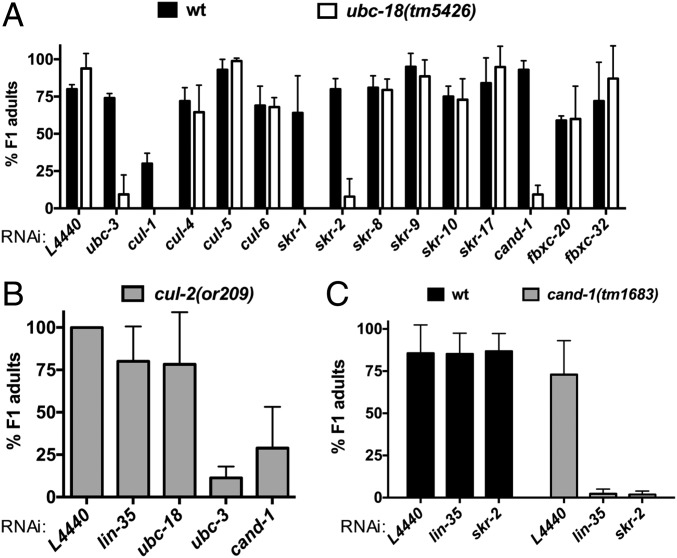
Fig. 2.
ubc-18 interacts synthetically with genes encoding SCF E3 ubiquitination machinery. (A) Quantification of synthetic lethal interactions with ubc-18. The percentage of F1 progeny of RNAi-fed animals that survive to adulthood is shown for WT (wt) and ubc-18(tm5426) strains (black and white bars, respectively). The rrf-3(pk1426) mutant served as the wild-type control. This mutant is wild type at the ubc-18 locus and reported to be RNAi-sensitive (49). Error bars are the SD between technical replicates in one representative experiment. The candidate screen was performed only once for genes that were not affected. Synthetic interactions with skr-1/2, cul-1, and cand-1 were observed in at least three independent experiments. (B) ubc-18 does not genetically interact with cul-2(or209ts). The percentage of F1 progeny of RNAi-fed animals that survived to adulthood is shown for cul-2(or209ts). Error bars are the SD between two independent experiments. (C) cand-1 genetically interacts with lin-35 and skr-2/1. The percentage of F1 progeny viable to adulthood is shown for N2 WT (wt, black bars) and cand-1(tm1683) mutant animals (gray bars) grown on each RNAi. Error bars represent the SD of at least three independent experiments.