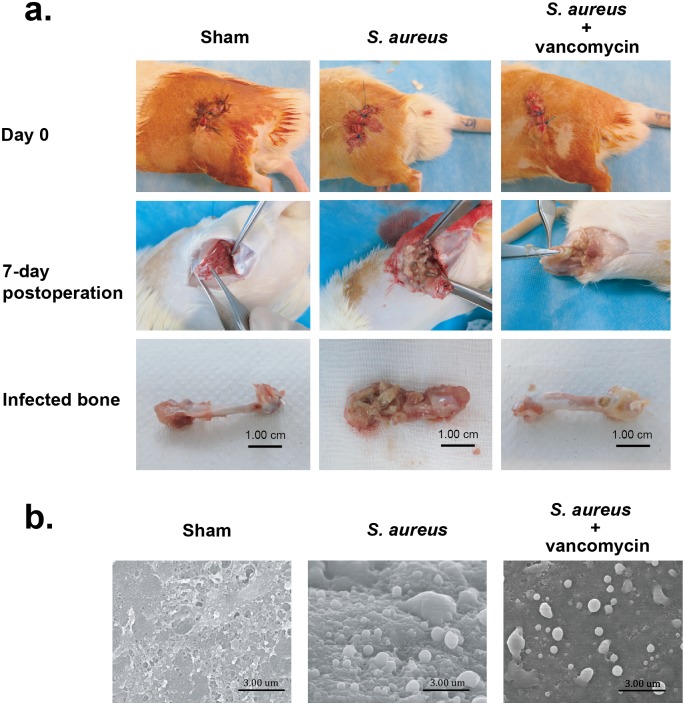
Fig 1. Surgical operation and S. aureus biofim formation in a rat PJI model.
(a) Rats were divided into three groups including the sham group, the S. aureus-infected group and the S. aureus-infected group receiving vancomycin treatment. All rats were sacrificed 7 days after surgery and the treated femurs were taken. Notably, severe bone osteolytic lesion with pus formation was observed in the S aureus-infected femur, but less osteolytic lesion was detected in the vancomycin-treated infection femur. (b) Scanning electron microscopy images of biofilm formation in femurs at day 7 post-infection. Biofilm formation and S. aureus cocci were more evident in the femur lumen of the S. aureus-infected group than those of the vanomycin-treated infection group (original magnification ×10,000).