Figure 3. Procedure to make a template clone.
(a) In the original clone, two unique sites recognized by two different type II restriction enzymes (labeled as TII-e1 and TII-e2) are selected in the gene of interest. The number x amino acid encoded by N2N3N4 (in red) is indicated by aax, or next amino acid by aax+1 (in green). A template fragment contains a TIIS DNA cassette (highlighted in blue box) in between aax and aax+1. All the cutting positions are indicated by arrows and complementary bases by apostrophe (’).
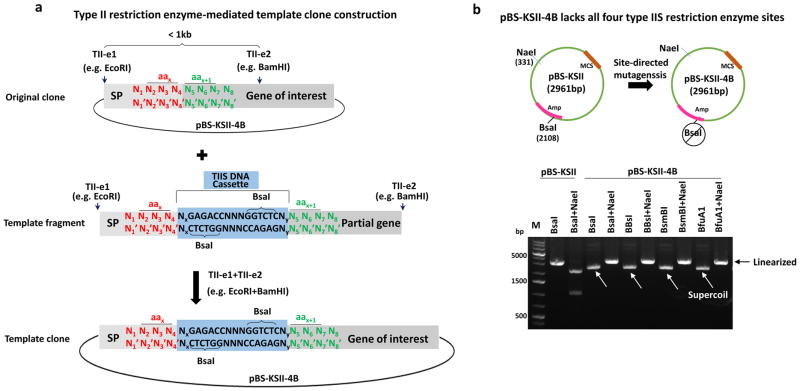
(b) pBS-KSII contains a multiple cloning site (MCS) and a BsaI in the ampicillin (Amp) coding gene, which was destroyed by site-directed mutagenesis to create pBS-KSII-4B. Wild-type pBS-KSII was linearized by BsaI and two overlapping fragments were released by BsaI and NaeI double digestion. pBS-KSII-4B does not have BsaI, BbsI, BsmBI, and BfuAI/BspMI and can be linearized by NaeI. Three brighter bands from GeneRuler 1kb plus DNA marker are labeled.