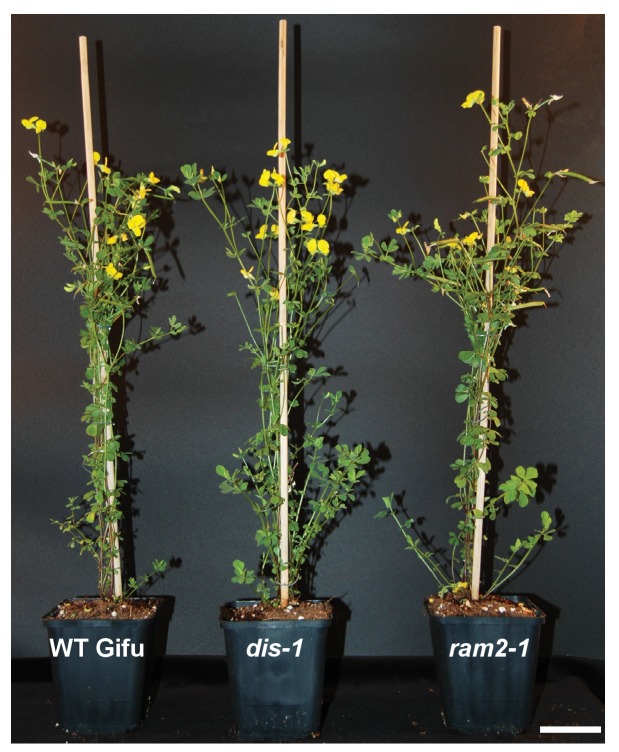
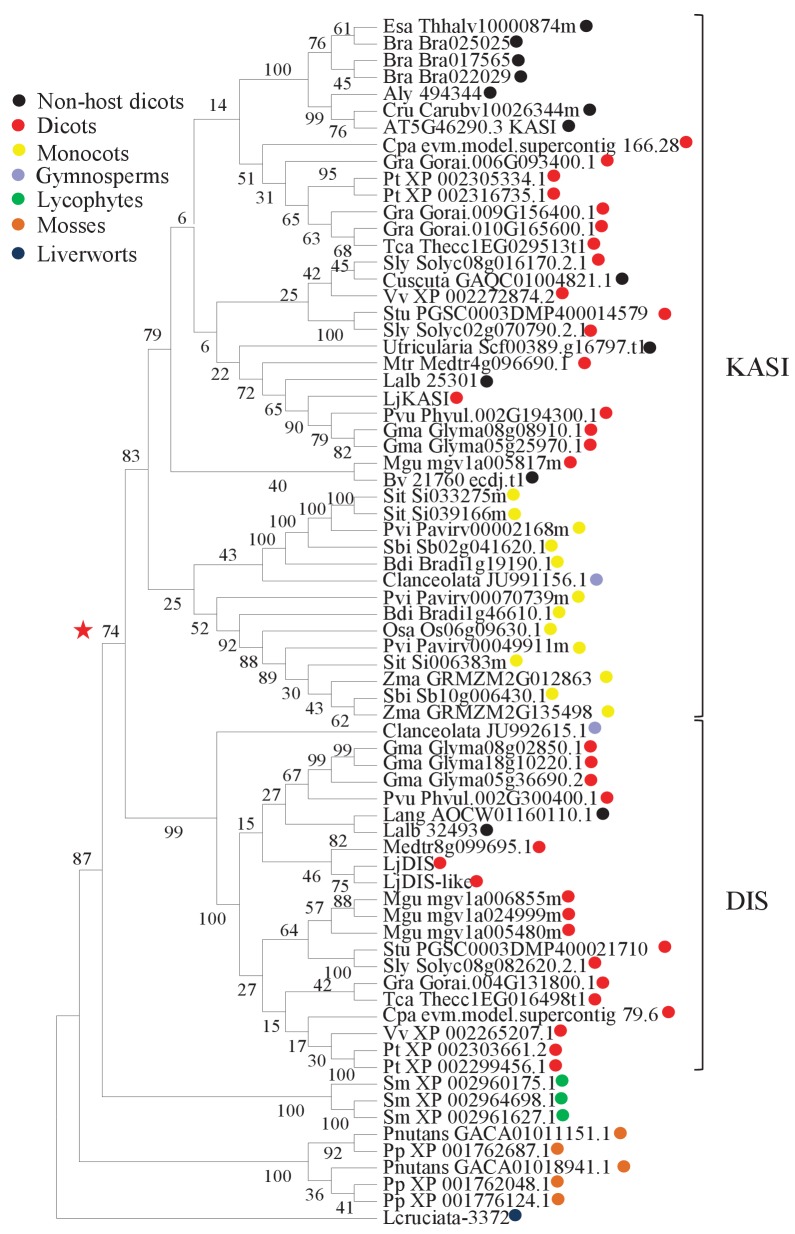
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree of KASI proteins in land plants.
Protein sequences were aligned using MAFFT. Phylogenetic trees were generated by neighbor-joining implemented in MEGA5 (Tamura et al., 2011). Partial gap deletion (95%) was used together with the JTT substitution model. Bootstrap values were calculated using 500 replicates. DIS likely originated before the angiosperm divergence (red star).
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29107.016