Figure 1. REMI for intraoperative guidance of lumpectomy.
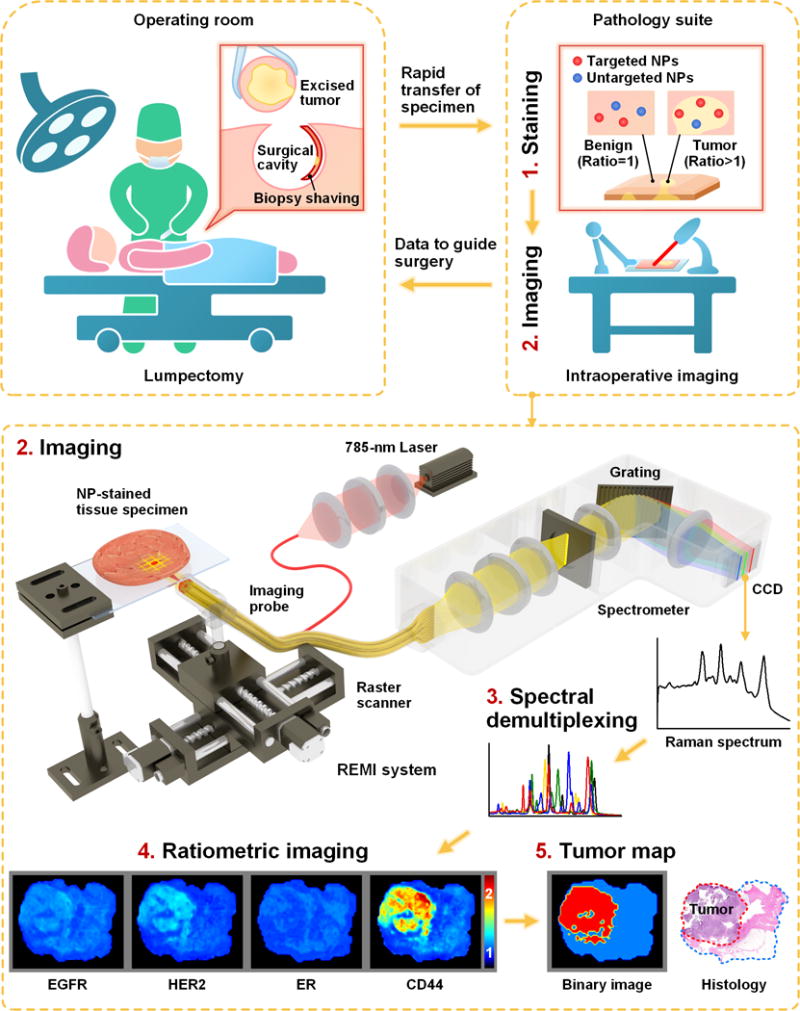
In a clinical implementation of REMI, freshly resected human breast tissues from lumpectomy procedures are immediately transferred to a pathology suite for intraoperative consultation. Each specimen is topically stained with a mixture of SERS NPs (multiple biomarker-targeted NPs and at least one untargeted control NP, step 1), followed by spectroscopic imaging of the surgical margin surface (step 2). The acquired SERS spectra are demultiplexed to determine the ratio of the targeted vs. untargeted NPs (step 3), which enables the quantification of various biomarker targets (e.g. EGFR, HER2, mER and CD44 in this study, step 4). REMI images of the individual biomarkers are combined to detect the presence of residual tumors at the surgical margin surfaces of the specimens (step 5). The entire REMI procedure (staining, rinsing, imaging, spectral demultiplexing) was performed within 10–15 min depending upon the size of the specimen.
