Figure 2.
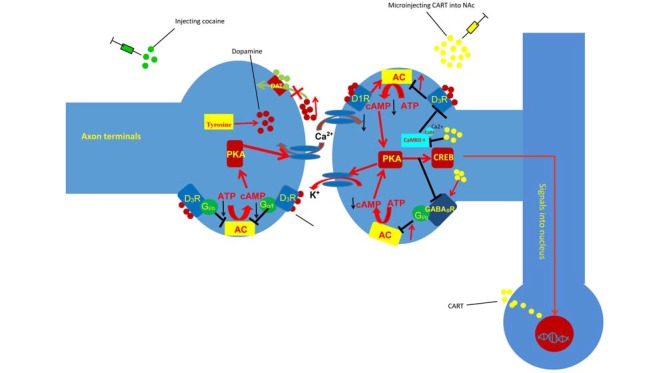
Injection of CART blunts the effect of cocaine on inhibitory G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). Cocaine can block the reuptake of DA and result in the accumulation of DA in the synaptic cleft. The accumulated DA can decrease the sensitivity of the D3 DA autororeceptors located on dopaminergic cells and favor somatodendritic DA release. Conversely, DA activates D1 DA heteroreceptors, desensitizes the D3 DA autoreceptors located on dopaminergic cells, and stimulates AC, resulting in increased intracellular cAMP levels. However, injecting CART into the NAc decreases the phosphorylation of CaMKIIα and D3R, which inhibits the activity of AC and reduces cocaine-induced LMA. D1R, dopamine D1 receptor; D3R, dopamine D3 receptor; PKA, protein kinase A; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; AC, adenylyl cyclase; DAT, dopamine transporter; CREB, cAMP-response element binding protein.
