Fig. 5.
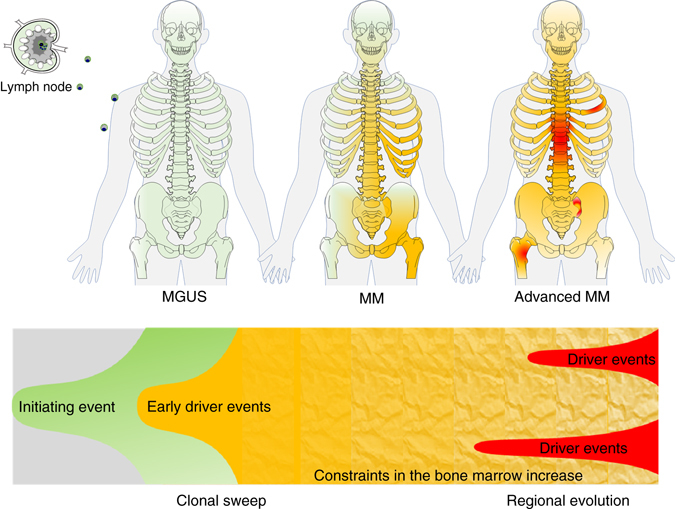
Regional differences in the context of a non-neutral evolutionary model considering spatial constraints. Ancestor clones (green) containing initiating aberrations such as hyperdiploidy or primary IgH translocations occupy the available plasma cell survival niches in the bone marrow leading to monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS). In the first phase, additional mutations result in subclones with increased fitness, and (multiple?) selective sweeps of advanced clones (yellow) finally replace MGUS/MM progenitors. In the second phase all available niches are occupied by advanced clones increasing the environmental constraints. At this stage the likelihood of invasion and sweeps is decreased favoring regional outgrowth of highly advanced clones (red). A more detailed description of this concept is provided in the main text
