Figure 1.
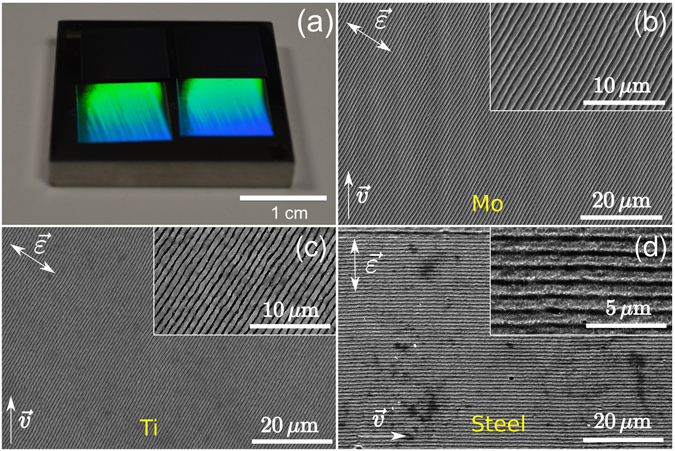
Demonstration of high regularity of LIPSS obtained in this study on several metals. Arrows indicate directions of laser field polarization () and laser beam scanning (). (a) Human-scale view of a stainless steel AISI 316 L sample covered with HR-LIPSS under ambient light conditions of the laboratory. Color arises from the diffraction of ambient light on the nanostructured material. (b–d) Respectively Secondary Electron Microscope (SEM) images of the Mo (effective pulse number N ~ 3.7, average fluence F = 0.69 J/cm2), Ti (N ~ 2.1, F = 0.59 J/cm2), and stainless steel (N ~ 2.1, F = 0.45 J/cm2) samples covered with HR-LIPSS. Steel comprises iron with 16.87% Cr and 10.05% Ni. Insets in Figs (b–d) show magnified views of corresponding images [2× in (b) and (c), 4× in (d)].
