Figure 1.
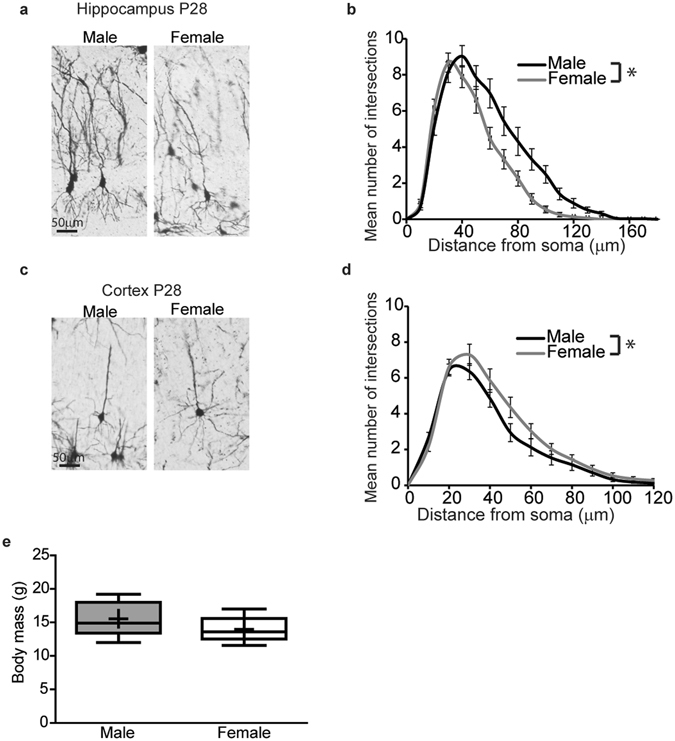
Dendritic arbors are more complex in male vs. female pyramidal neurons in the CA1 hippocampus while the opposite is true for pyramidal neurons in the adjacent somatosensory cortex in vivo. Representative photomicrographs of Golgi stained neurons (a,c) and Sholl analyses (b,d) of the basilar dendritic arbors in Golgi stained pyramidal CA1 hippocampal neurons (a,b) and adjacent pyramidal somatosensory cortical neurons (c,d) from postnatal day (P) 28 male and female C57BL/6 J mice. Body mass of P28 male and female mice (e). Data in panels b and d presented as mean ± SEM, (n = 35 male and 31 female hippocampal neurons, n = 34 male and 34 female cortical neurons from five animals of each sex from independent litters). In the box plots in panel e, “+” indicates the mean; whiskers, the 10–90th percentile; n = 5 litter-independent mice per sex. Significant differences were determined using a mixed effects model for Sholl data (b, d) and Student’s T-test for body mass (e). Asterisk indicates a significant difference between groups at p ≤ 0.05.
