Fig. 4. Using a SSB-GFP fusion protein to assess bacterial replication in tissue.
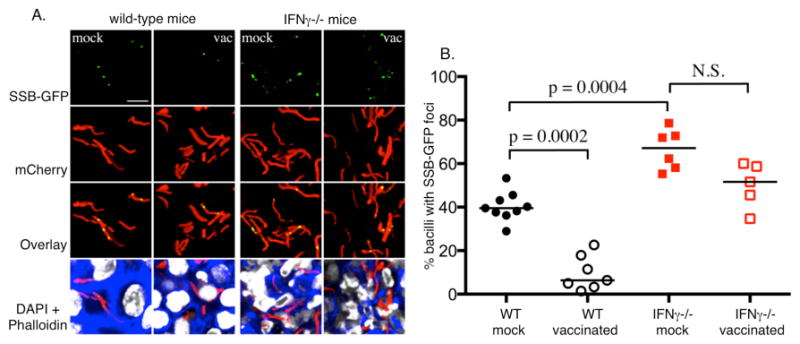
Naïve (mock) and vaccinated (vac) wild-type and IFN-γ-deficient mice were challenged with Mtb expressing mCherry and SSB-GFP, as reported previously (16). The mice were sacrificed at 28 days and the lung tissue analyzed by confocal microscopy. A. Shows confocal images from the infected lung tissue demonstrating the presence of green foci amongst some of the bacteria in the section. The presence or absence of GFP foci within the bacteria was scored manually. B. A scatter plot of the % of GFP foci-positive bacteria in each mouse in each group. The dots each represent a single mouse. The horizontal bars represent the median value for each group and p-values were obtained with a Mann-Whitney statistical test. The graph indicates that the number of SSB-GFP foci-positive bacteria was inversely proportional to the robustness of the immune response. This suggests that replication was best controlled in vaccinated mice, and least controlled in mice deficient in the macrophage-activating cytokine IFN-γ.
