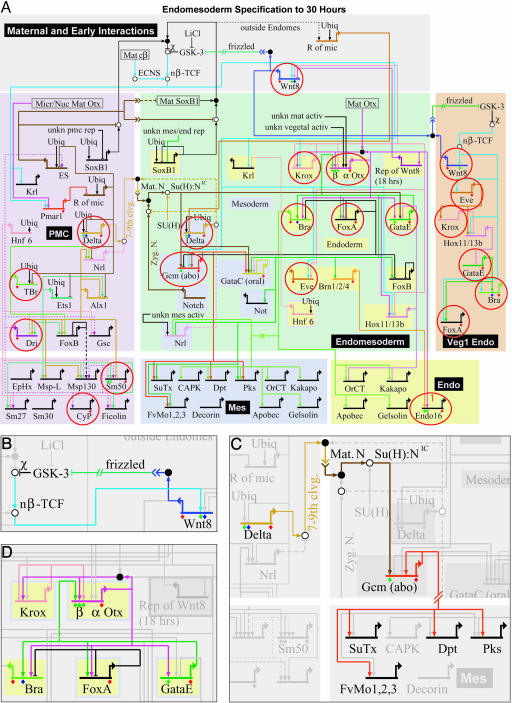
Fig. 1.
GRN for endomesoderm specification in sea urchin embryos. (A) GRN for period from initiation of zygotic regulatory control shortly after fertilization to just before gastrulation (≈4–30 h). The short horizontal lines represent relevant cis-regulatory modules of indicated genes on which the color-coded inputs impinge. The sources of these inputs are other genes of the GRN, as indicated by the thin colored lines. Small open and filled circles represent protein–protein interactions that occur off the DNA and are not included explicitly in the GRN, the objective of which is to display the predicted genomic regulatory organization responsible for spatial and temporal expression of the genes it includes. For symbolism, explanations, and access to the biotapestry software by which the GRN is built and maintained, see http://sugp.caltech.edu/endomes/webStart/bioTapestry.jnlp, where the current version of GRN is posted or contact E.H.D. The red circles indicate genes for which genomic cis-regulatory modules have been isolated and shown to generate the relevant spatial and temporal patterns of gene expression of the endogenous genes. (B) The cis-regulatory programming of the wnt8 loop, from ref. 24. Experiments demonstrate that the cis-regulatory system includes Tcf sites that are required to maintain expression and that respond to the β-catenin–Tcf input (nβ-TCF); as is well known, reception of the Wnt8 signal ligand causes intracellular formation of nuclear β-catenin–Tcf complex in the recipient cells. Thus, the endomesodermal cells are engaged in a self-stimulating, positive reinforcement of expression of Tcf-responsive genes (see A). (C) The cis-regulatory programming responsible for reception by adjacent presumptive mesodermal cells of a Delta signal emitted by skeletogenic cells and for activation of pigment cell differentiation genes (29); these are SuTx (Sulfotransferase), Dpt (Dopachrome tautomerase), Pks (Polyketide synthetase), and FvMo (Flavine-containing monoxigenase). The Delta signal is received by a Notch receptor that together with a Supressor of Hairless [Su(H)] transcription factor already present in these cells transmits a permissive input to the cis-regulatory module of the gcm regulatory gene. These relationships were established experimentally in gene transfer studies by using a mutant Su(H) factor and by mutational analysis of the gcm cis-regulatory module (A. Ransick and E.H.D., unpublished data). After activation, gcm locks itself on by autoregulation. (D) Endoderm specification feedback loop. As discussed in the text and in more detail elsewhere (4, 19, 56), this “kernel” of the GRN is conserved without significant change in starfish, a very distantly related echinoderm. It has the functions of initially activating regulatory genes in the presumptive endoderm as a function of krox and β-otx activation; thereby activating a pleiotropic endoderm regulator, gatae, then locking in gatae expression by establishment of feedback to a β-otx cis-regulatory module, and stably activating the gut regulatory genes foxa and brachury.