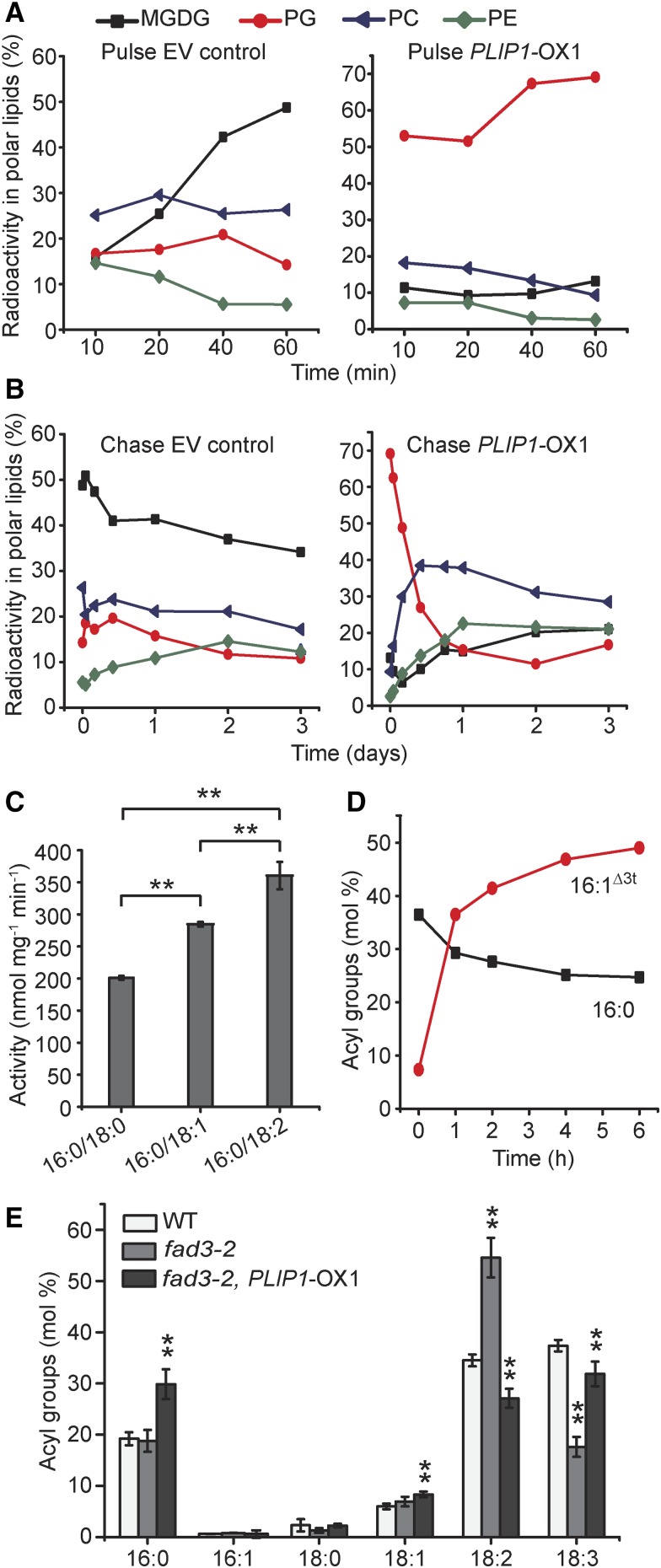
Figure 6.
PLIP1 Precursor-Product Relationships in PLIP1 Overexpression Plants.
(A) and (B) In vivo pulse-chase acetate labeling of lipids in wild-type and PLIP1-OX1 plants. The length of the [14C]-acetate labeling pulse was 60 min (A), after which medium was replaced with nonlabeled free acetate to initiate the chase with a duration of three days (B). The fractions of label in all polar lipids are given as percentages of total incorporation of label in polar lipids. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results, and one representative result is shown.
(C) Activity of purified recombinant PLIP1 on PC with different sn-2 acyl groups. PC containing 16:0/18:0, 16:0/18:1, and 16:0/18:2 were used as substrates. n = 4, ±sd. Student’s t test was applied (**P < 0.01).
(D) PLIP1 enzyme activity preference for molecular species of phosphatidylglycerol isolated from N. benthamiana leaves. Acyl groups of lyso-phosphatidylglycerol are shown as molar percentages of total acyl groups at any given time point. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results and data from one representative experiment are shown.
(E) Relative acyl composition of PC in wild-type, fad3-2, and fad3-2 PLIP1-OX1 plants. Leaf lipids were extracted and isolated by TLC and fatty acid methyl esters derived from the lipids were analyzed by GC. Mature leaf samples harvested from one plant were taken as one biological repeat; n = 4, ±sd. Student’s t test was applied (**P < 0.01).