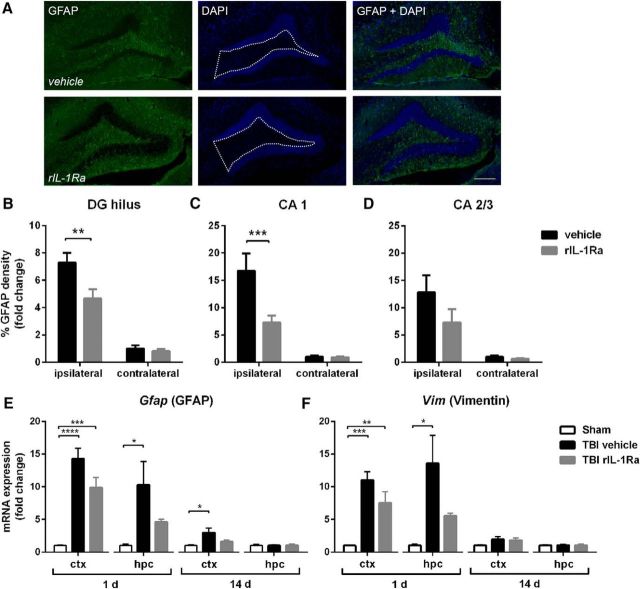
Figure 4.
rIL-1Ra treatment attenuates subacute astrogliosis after pTBI. Quantification of GFAP+ reactivity from immunofluorescent labeling with DAPI (A) at 2 weeks post-injury, revealed a robust increase in astrogliosis in the ipsilateral DG hilus (B; two-way RM ANOVA injury × drug interaction: F(1,17) = 5.04, p = 0.04; post hoc, p < 0.01) and CA1 (C; injury × drug interaction: F(1,17) = 8.76, p < 0.01; post hoc, p < 0.001) of vehicle-TBI mice, which was attenuated in rIL-1Ra-TBI mice. n = 9–10/group. Scale bar, 200 μm. Region-of-interest indicated by dotted white line in A. This was reflected by changes in gene expression of astrocyte markers Gfap (E) and Vim (F), which were robustly elevated at 1 d after injury in the cortex (Gfap: F(2,12) = 28.06, p < 0.0001; Vim: F(2,12) = 17.45, p < 0.01) and hippocampus (Gfap: F(2,12) = 5.04, p = 0.03; post hoc, p < 0.05; Vim: F(2,12) = 6.50, p = 0.01). n = 5/group; *p < 0.01, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.