Fig. 4.
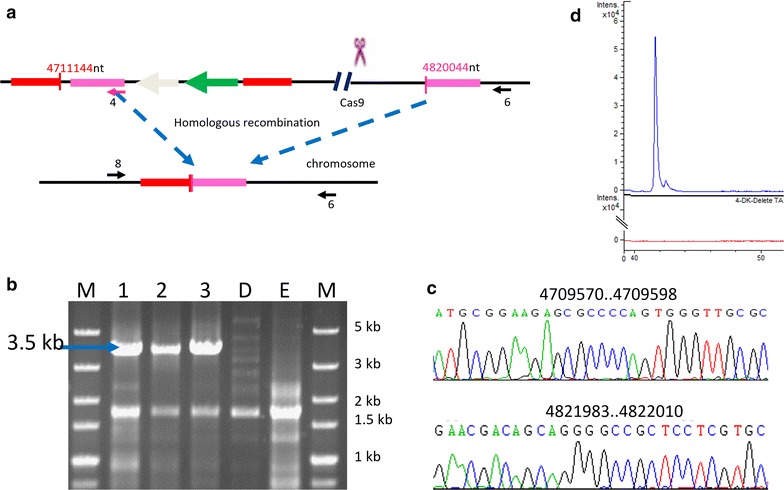
Large fragment deletion of the myxovirescin biosynthetic gene cluster in M. xanthus DK1622. a Schematic diagram for the deletion program. Left and right homologous arms are shown in red and pink rectangles, respectively. Gray and green arrows represent galK gene and kanR gene, respectively. b Identification of mutant strains by agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR product. The PCR primers 8 and 6 (referred to the a) yielded the 3.5-kb positive band (indicated by blue arrow) in three independent mutants (lanes 1–3), but not in the negative controls of DK1622 (lane E) and DKpBJ11-tsg112 (lane D). c Chromatograms of the 3.5-kb PCR product DNA sequences, sequenced using the primers 8 and 6 as the sequencing primers. Since plasmid pBJ11 contains the nucleotide sequence crossing the deleted chromosomal region, we sequenced the flanked region at two ends of the 3.5-kb PCR product. d EIC of myxovirescin A ([M+H]+ m/z 624.44) from the DK1622 (blue) and mutant (red)
