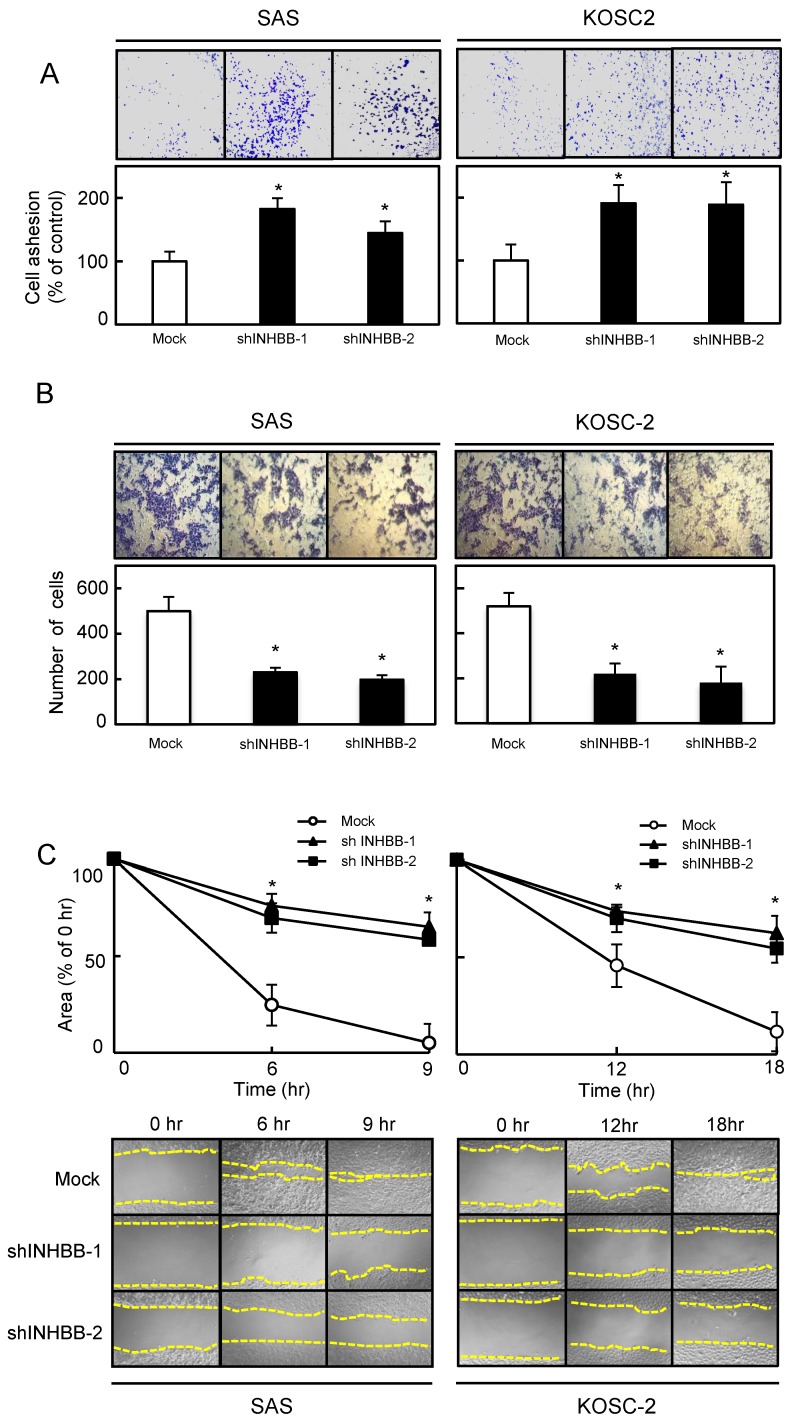
Figure 4.
Functional assays. (A) Adhesion assay of Mock and shINHBB cells (SAS and KOSC-2-derived transfectants). To evaluate the adhesion ability of shINHBB, the cells are seeded on collagen I-coated 96-well plates at a density of 2 ×104 cells/well and allowed to adhere for 1 hour. After crystal violet staining, the numbers of stained cells are measured using a microplate spectrophotometer (absorbance at 540 nm and at 405 nm to subtract background). The cellular adhesion of the shINHBB cells are increased significantly (P < 0.05) compared with the Mock cells. The results are expressed as the means ± SEM of values from three assays (*P < 0.05, Student's t-test). (B) Invasiveness assay of Mock and shINHBB cells (SAS and KOSC-2-derived transfectants). To evaluate the effect of INHBB knockdown on invasiveness, the cells are seeded on Matrigel-coated Transwell inserts (8 μm pores) at a density of 2.5×105 cells/well in serum-free medium. Serum-supplemented medium was added in the lower chamber as a chemoattractant. After incubation at 37°C for 48 hours, cells that penetrated through the pores are fixed, stained, and counted using a light microscope at ×100 magnification. The number of shINHBB cells penetrating through the pores is decreased significantly (*P < 0.05, Student's t-test) compared with the Mock cells. The mean value is calculated from data obtained from three separate chambers. (C) Migration assay of Mock and shINHBB cells (SAS and KOSC-2-derived transfectants). To evaluate the effect of INHBB knockdown on migration, uniform wounds are made in confluent cultures of the shINHBB and Mock cells and the extent of closure is monitored visually every 3 hours for 18 hours. The mean value is calculated from data obtained from three separate chambers. The wound area is decreased significantly (*P < 0.05, Student's t-test) in the Mock cell culture after 9 or 12 hours, whereas a gap remains in the shINHBB cells.