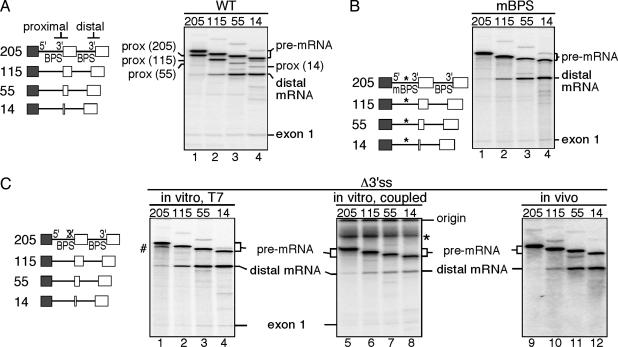
Fig. 1.
Proximal exon sequences suppress use of the distal 3′ splice site. (Left) The structures of the pre-mRNAs derived from the wild-type (A), mBPS (B), and Δ3′ss (C) constructs are shown. Exonic sequences are represented by boxes; β-globin intronic sequences are represented by a straight line. The numbers refer to the length of the duplicated portion of exon 2. (A) For the proximal spliced products (prox), the lengths of the internal exon sequences are indicated in parentheses. (B) *, The mBPS. (C) The Δ3′ss pre-mRNAs were presynthesized by using a T7 promoter and then spliced in vitro in HeLa nuclear extract (Left), transcribed by using a cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter and concomitantly spliced in HeLa nuclear extract (Center), or presynthesized by using a T7 promoter and then microinjected in Xenopus oocyte nuclei to be spliced in vivo (Right). The deletion of the pyrimidine tract at the proximal 3′ splice site is indicated by an X-marked 3′. #, Pre-mRNA breakdown products; *, nonspecific signal.