Figure 6. Identification of the Pds5B-binding region in Scc1.
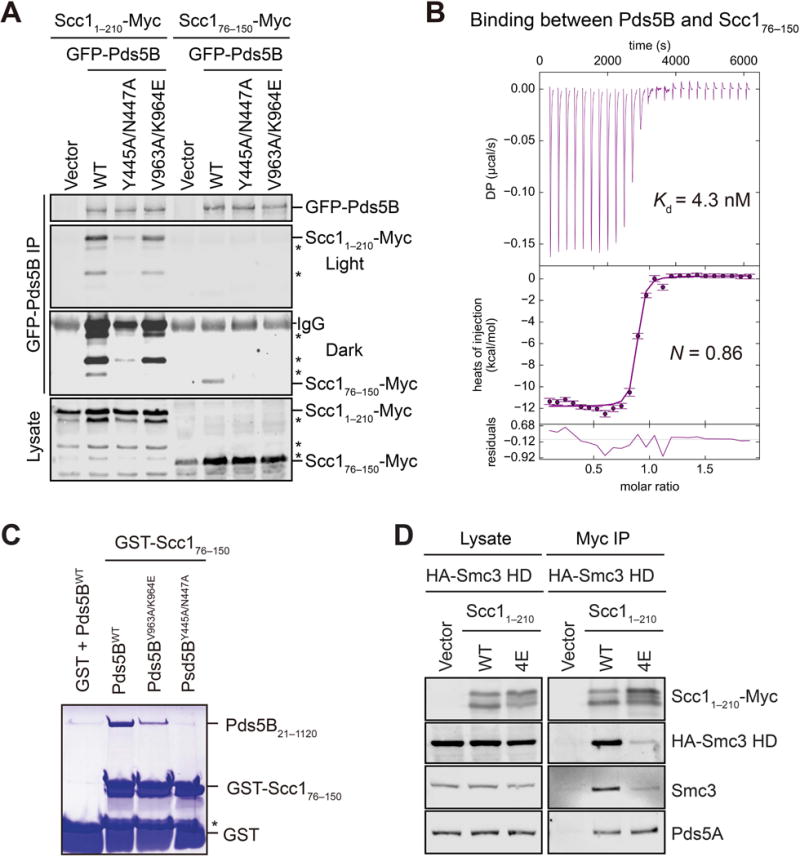
(A) Immunoblots of lysate and anti-GFP immunoprecipitates (IP) of HeLa cells transfected with the indicated Scc1-Myc and GFP-Pds5B plasmids. Asterisks indicate N-terminally truncated forms of Scc11–210-Myc. WT, wild type.
(B) ITC curves of the binding between purified recombinant Pds5B21–1120 and Scc176–150, with the dissociation constant (Kd) and binding stoichiometry (N) indicated. DP, differential power.
(C) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel of recombinant human Pds5B21–1120 wild type (WT) or mutant proteins bound to beads containing GST or GST-Scc176–150. Asterisk indicates a proteolytic fragment of GST-Scc176–150.
(D) Anti-Myc, anti-HA, anti-Smc3, and anti-Pds5A blots of lysates and anti-Myc immunoprecipitates (IP) of HeLa cells that were transfected with plasmids encoding HA-Smc3 HD and the indicated Scc11–210-Myc plasmids. WT, wild type; 4E, L53E/L59E/Y67E/L74E.
