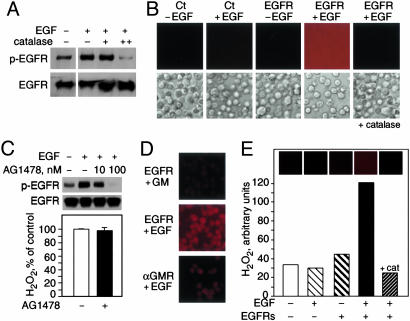
Fig. 5.
EGFR–ligand interaction generates extracellular H2O2 in cells and with purified proteins. (A) EGF-induced phosphorylation of EGFR in A431 cells treated with catalase. Phosphorylated EGFR (p-EGFR) (Upper) and unphosphorylated EGFR (Lower) were detected by immunoblotting. (B) Fluorescence microscopy detection of extracellular H2O2 in 293T cells untransfected (Ct) or transfected with EGFR and incubated in Amplex Red for 30 min with or without 100 nM EGF. Corresponding light microscopy images are provided in Lower. (C) EGF-induced phosphorylation of EGFR-transfected 293T cells treated with AG1478. (Upper) Proteins were detected as in A.(Lower) EGFR–ligand-dependent H2O2 generation in 293T cells treated with or without AG1478. (D) Extracellular H2O2 generation by fixed 293T cells transfected with EGFR or αGMR and treated with EGF or GM, as detected by fluorescence microscopy. (E) Purified human soluble EGFR was incubated in Amplex Red with or without EGF and H2O2 detected by fluorescence microscopy. cat, catalase.