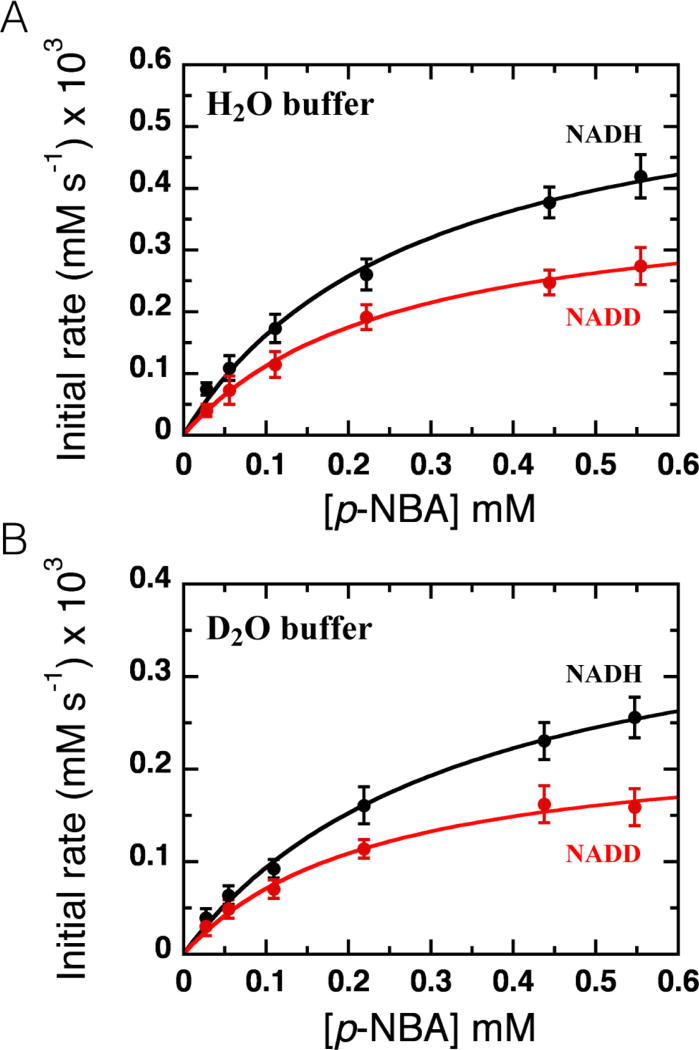
Figure 3. Kinetic isotope effects on NR’s rapid reaction kinetics.
(A) Reductive half-reaction of NR Kinetic traces of the reduction of NR with NADH (●) or [4R-2H]NADH (○) at 4°C (17.5 µM and 100 µM after mixing). Parameters of the fits appear in Table 2. (B) Oxidative half-reaction of NR reduced using NADH (●) or [4R-2H]NADH (○) then mixed with p-NBA (13 µM, 13 µM, 2 mM after mixing). (C) Water access to the active site revealed by comparison of the oxidative half reaction of reduced NR in H2O buffer with 9% (w/v) glycerol mixed with p-NBA equilibrated in the same buffer (17.5 µM and 2 mM after mixing, kobs = 11.5 ± 0.1 s−1 , ●) vs. the reaction with p-NBA equilibrated in D2O buffer (kobs = 9.0 ± 0.1 s−1, ○) vs. the result of mixing NR with p-NBA both in D2O buffer (kobs = 6.1 ± 0.1 s−1, +). Triangles (Δ) show the reaction of reduced NR and p-NBA both equilibrated in H2O buffer without 9% glycerol. Only every 20th data point is shown for clarity.