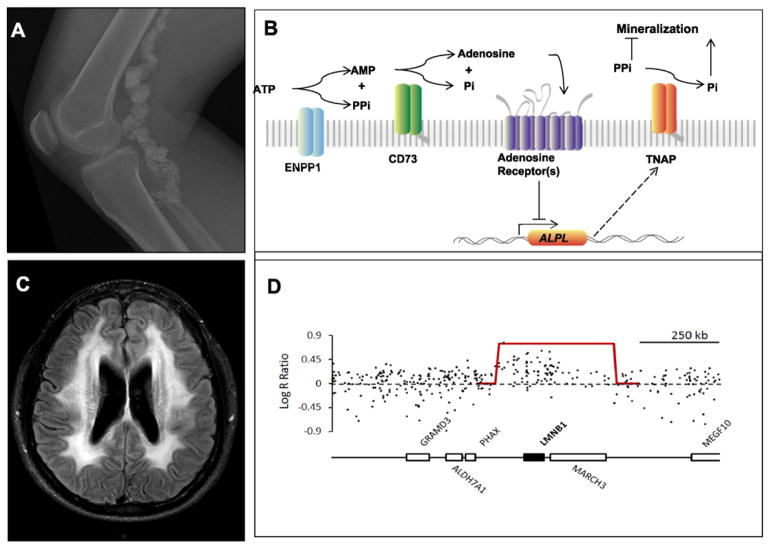
Fig. 3.
Newly recognized mechanisms of disease. (A) Plain radiograph of a patient showing extensive, irregular calcification and dilatation of the femoral and popliteal arteries [7]. (B) Purinergic pathway at the surface of vascular endothelial cells. Normally, CD73 (encoded by NT5E, defective in ACDC) converts adenosine monophosphate to adenosine and inorganic phosphate (Pi). Adenosine binds to the adenosine receptor, trophically inhibiting alkaline phosphatase (APL) expression. When CD73 is absent, ALP is increased and converts pyrophosphate (PPi, an inhibitor of calcification) to Pi (a stimulator of calcification). In vitro studies showed that NT5E mutant fibroblasts calcified under osteogenic conditions, and the calcification could be reversed by adenosine or an APL inhibitor. (Courtesy of Shira Ziegler, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.) (C) Brain MRI showing leukodystrophy in brainstem and middle cerebellar peduncles of a patient with duplication of LMNB1. (D) Log R ratios of fluorescent intensity of SNPs on chromosome 5q. A contiguous group of SNPs has higher intensity, reflecting a duplication, i.e., three total copies rather than two. The gene annotation of the region indicates that LMNB1 is encompassed by the duplication.