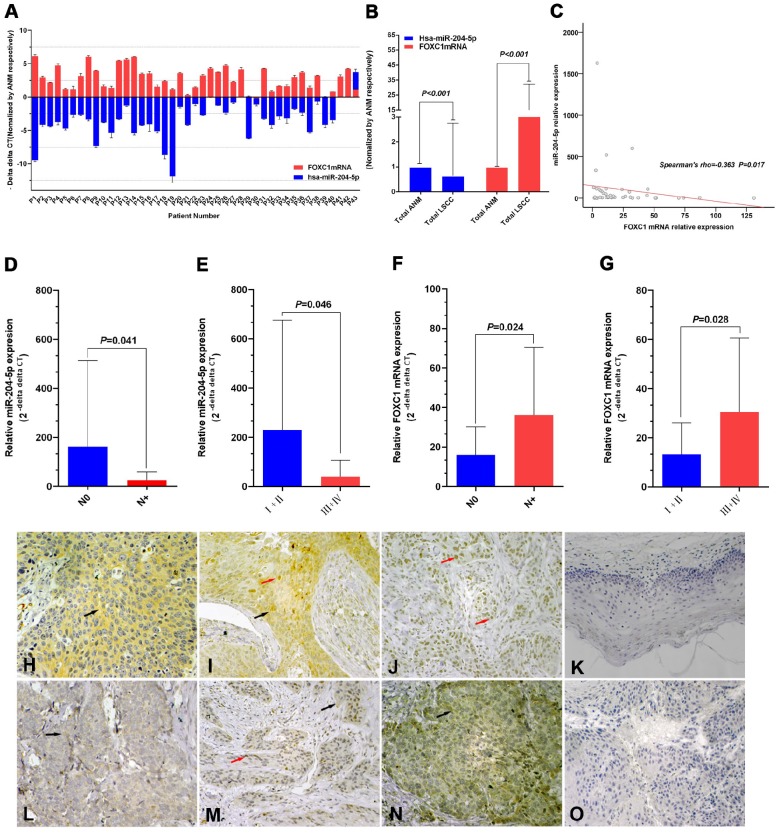
Figure 1.
Expression of miR-204-5p and forkhead box C1 (FOXC1) in LSCC tissues. A: Quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) analysis of relative RNA expression of miR-204-5p and FOXC1 in 43 LSCC tissue samples and corresponding adjacent normal mucosa (ANM). Data are presented as -ΔΔCT (mean±SD). B: qPCR analysis of relative RNA expression of miR-204-5p and FOXC1 in all 43 LSCC samples and corresponding ANM. C: Correlation of expression between miR-204-5p and FOXC1 RNA levels in LSCC tissues (r=-0.363, P=0.017). D-E: Relative RNA expression of miR-204-5p by lymph node and clinical staging in LSCC and ANM samples. F-G: Relative mRNA expression of FOXC1 by lymph node and clinical staging in LSCC and ANM samples. H-J: Immunohistochemical staining of the FOXC1 protein in LSCC tissue sections. Strong cytoplasmic FOXC1 staining in LSCC cells (H). Strong nuclear and cytoplasmic FOXC1 staining in LSCC cells (I). Strong nuclear FOXC1 staining in LSCC cells (J). K: Immunohistochemical staining of FOXC1 protein in adjacent normal mucosa. L: Low FOXC1 expression in tissues with high miR-204-5p expression; weak positive granular deposition in the cytoplasm of LSCC cells. M: Low FOXC1 expression in tissues with high miR-204-5p expression; weak positive granular deposition in the cytoplasm and nuclei of LSCC cells. N: Pronounced FOXC1 expression in tissues with low miR-204-5p expression; notable positive granular deposition in the cytoplasm of LSCC cells. O: FOXC1 negative control section (primary antibody replaced by PBS during the IHC process of LSCC tissue section). Black arrows show positive cytoplasmic staining; red arrows show positive nuclear staining; magnification 40×10. Data are presented as the mean ± SD.