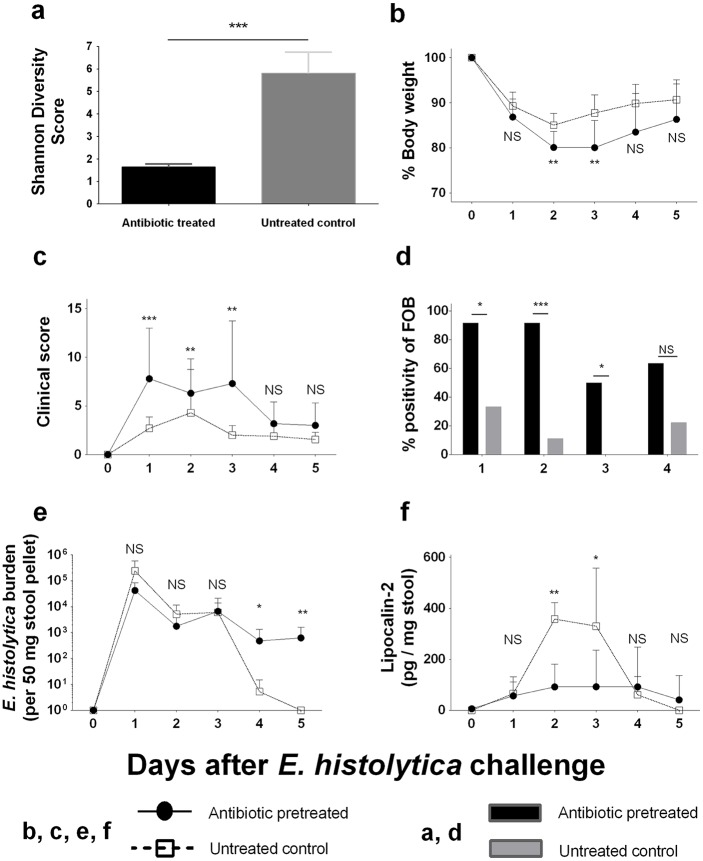
Fig 2. Antibiotic pre-treatment rendered C57BL/6 mice susceptible to E. histolytica colitis.
(a) The Shannon diversity index of stool samples collected from antibiotic treated mice (n = 10) was compared with those from untreated control (n = 10) (C57BL/6 mice which were not challenged with E. histolytica). Then, they were infected with 2 x 106 E. histolytica trophozoites intracecally. (b, c) Body weight changes and clinical illness score were measured for assessing systemic disease severity. (d) Fecal occult blood was examined for assessing intestinal damage. (e) Parasite burden in stool was assessed by qPCR. (f) Lipocalin-2 (Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin) in stool was measured for assessing neutrophil mediated gut inflammation. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 by Welch’s unequal variance t-test (a, b, e& f), Mann-Whitney U-test (c) or chi-squared test (d). NS, not significant. Error bars represent s.e.m.