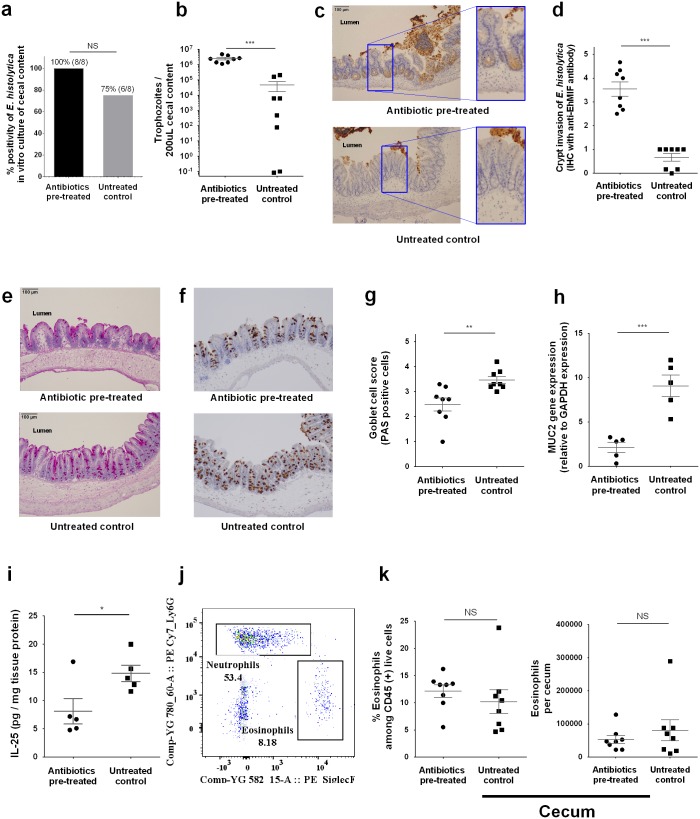
Fig 3. Antibiotic treatment promoted E. histolytica invasion with disrupted mucosal barrier.
Parasite invasion and mucosal barrier disruption upon E. histolytica challenge were assessed using cecal tissue or cecal content at 24 hours after challenge. (a, b) Parasite burden in cecal content was measured by qPCR and ex vivo culture positivity was also assessed by putting 200 μL of cecal content to TYI media (n = 8 per group). (c-g) E. histolytica induced epithelial barrier disruption was assessed by immunohistochemistry staining of cecal tissue targeting E. histolytica derived secreted protein, E. histolytica migration inhibitory factor (EhMIF) (representative picture in Fig 3c). Mucin containing goblet cells were stained by Periodic acid-Schiff and immunohistochemistry staining of cecal tissue targeting MUC2 (data are presented as representative pictures (e, f). Data are also presented as mean value of histology score blindly scored by three independent observers from similarly conducted two independent experiments, n = 8 per group (d, g)). (h) Cecal lysate at 24 hours after E. histolytica challenge was tested for Muc-2 gene expression by qRT-PCR and is shown normalized to the GAPDH housekeeping gene. (i) Cecal cytokine was assessed by lysing 50 mg of cecal sections and quantifying protein via ELISA, and shown normalized to total protein concentration (n = 5 per group (g, h)). (j,k) whole cecal tissue was isolated and processed to a single cell suspension and stained for flow cytometry. Eosinophils (CD45+ CD11b+ SiglecF+) were quantified and shown as ratio to CD45+ subsets or cell number in whole cecum (n = 8 per group). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 by Welch’s unequal variance t-test (a, h, i, & k), Mann-Whitney U-test (d & g) or chi-squared test (b). NS, not significant. Error bars represent s.e.m. Eh MIF, E. histolytica migration inhibitory factor.