Fig. 4.
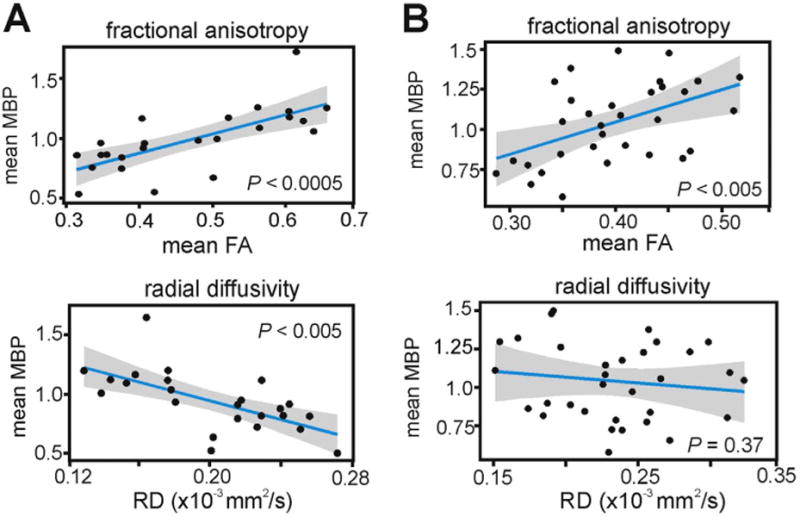
RD does not correlate with myelination in a subset of WM tracts. (A) Within a subset of mainly commissural WM tracts, FA and RD were significantly correlated with MBP immunofluorescence. (B) RD did not correlate with MBP in the remaining WM tracts, indicating that other factors such as fiber architecture, axon density, or axon caliber may be more significant contributors to diffusion anisotropy and directional diffusivity in these WM regions. Linear regressions are shown with 95% confidence intervals. Each data point is a mean MBP immunofluorescence and mean FA measure from a single WM ROI, in one mouse brain. MBP immunofluorescence values were normalized to a global average.
