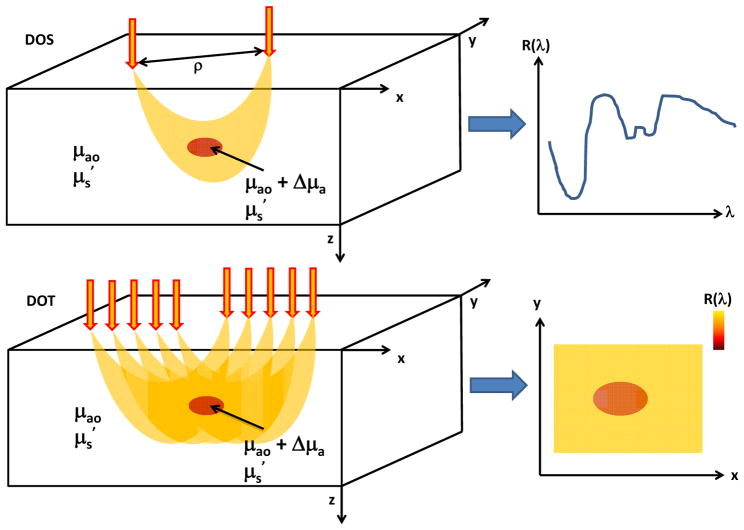
Figure 3.
Schematics of common DOS (top) and DOT (bottom) measurement setups. In DOS, light is delivered to the tissue via a source fiber and backscattered photons are detected via a detector fiber separated some distance ρ from the source. This source-detector separation plays a key role in controlling the region of tissue sampled by the majority of the photons. DOS measurements provide the reflectance at different wavelengths, enabling detection of spectral features of tissue absorption and scattering. In DOT, reflectance measurements at multiple source-detector pairs are employed to enable reconstruction of a two-dimensional map of the reflectance (and hence, absorption and scattering) at each wavelength.