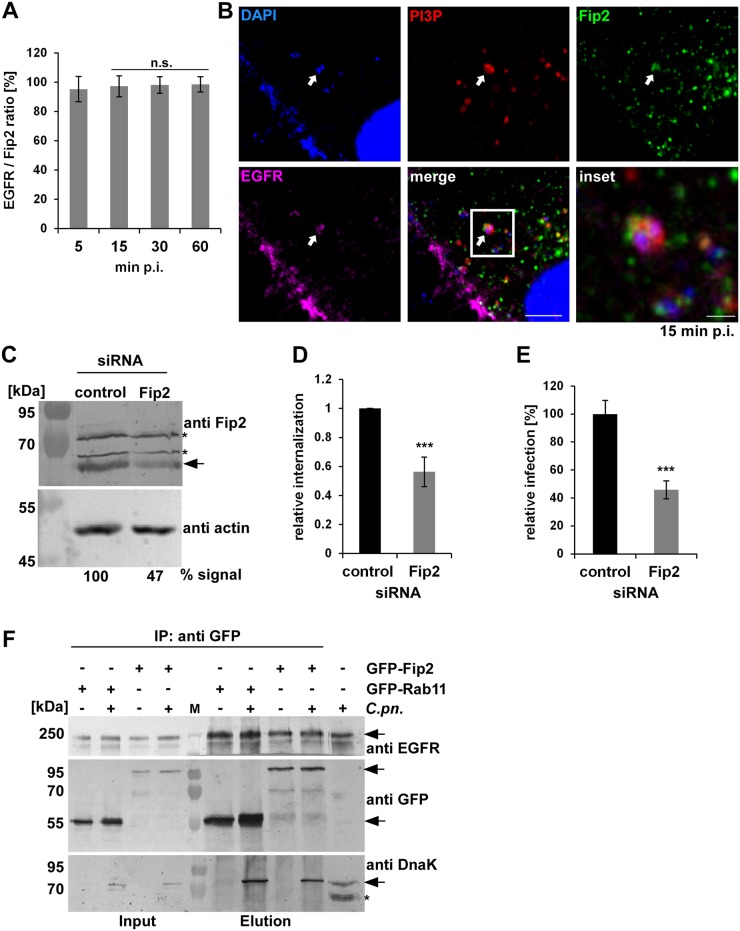
Fig 4. The Rab11/Rab14 adaptor Fip2 is recruited to early C. pneumoniae inclusions.
(A) Quantification of colocalization of Fip2 and EGFR with chlamydial EBs at 5–60 min p.i. in cells transiently transfected with GFP-Fip2 (n = 3). (B) Confocal images of colocalization of EBs (stained by DAPI) with GFP-Fip2, PI3P and EGFR (visualized by mCherry-FYVE and anti EGFR and anti-rabbit Alexa647, respectively) at 15 min p.i. White arrows indicate colocalization, the white box marks the area enlarged in the inset. Bar 10 μm. Bar in inset 1 μm. (C) Immunoblot analysis of cells transiently transfected for 72 h with control or Fip2 siRNA. Samples were lysed in phospho-Lysis buffer, subjected to SDS/PAGE and probed with antibodies against Fip2 to monitor knockdown; β-actin served as the loading control. The pixel intensity of bands was analyzed with ImageJ. The arrow marks the Fip2 protein band, unspecific bands detected by the Fip2 antibody are indicated by asterisks. (D, E) Quantification of EB internalization or infection after transfection for 72 h with control or Fip2 siRNA. (D) Relative internalization levels were measured by q-PCR of isolated DNA using primers specific for human GAPDH and chlamydial 16S rRNA at 2 hpi (n = 6). (E) Quantification of infection analyzed microscopically as described before (n = 4). (F) Co-IP of HEp-2 cells stably expressing GFP-Rab11 or GFP-Fip2 after infection for 15 min. Chlamydia-containing endosomes were isolated and subjected to immunoprecipitation using a GFP antibody coupled to ProteinG Dynabeads. Input and elution samples from IP and a control sample of cells infected with C. pneumoniae for 72h (last lane) were fractionated by SDS/PAGE and probed with anti-EGFR, anti-GFP and anti-DnaK antibodies. Arrows mark specific protein bands, the asterisk indicates unspecific bands detected in the infected cells by the DnaK antibody. *** P value ≤0.001.