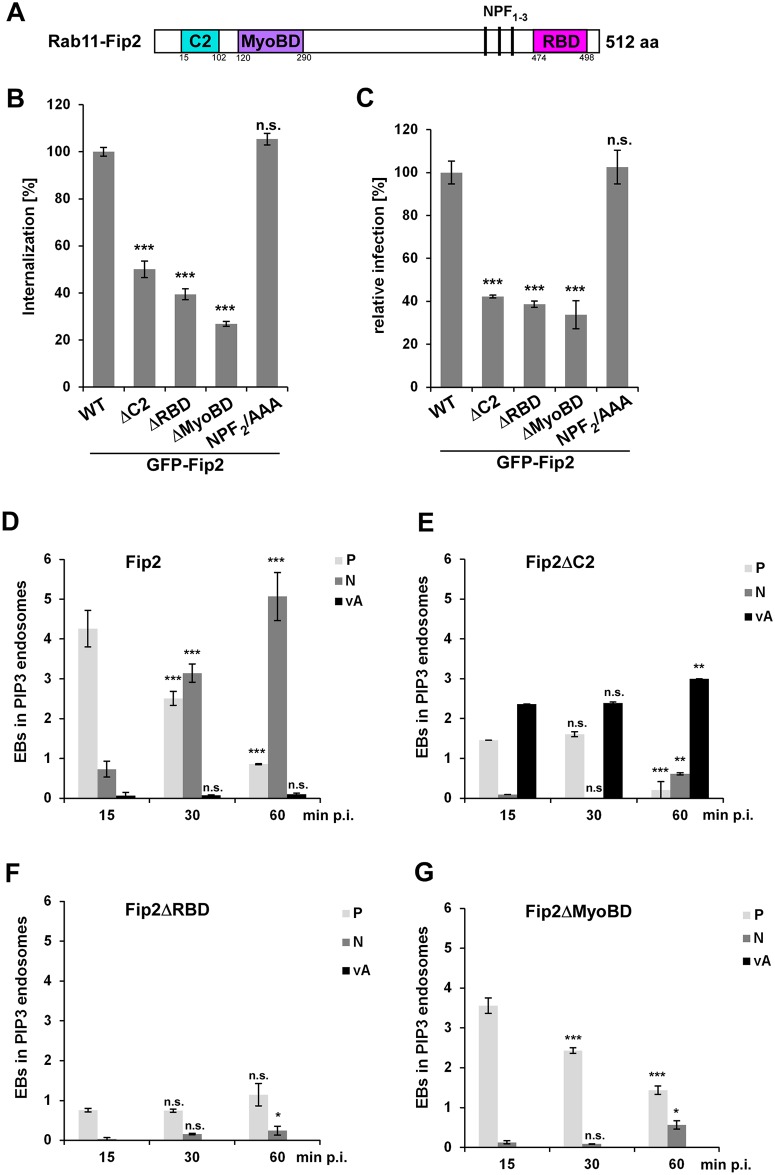
Fig 5. The Rab11-binding domain of Fip2 is essential for C. pneumoniae infection.
(A) Schematic representation of Fip2. (B, C) Quantification of EB internalization (B) or chlamydial infection (C) in HEp-2 cells stably expressing the indicated GFP-Fip2 mutant variants. (B) Analysis of C. pneumoniae EB internalization at 2 hpi in 30 individual cells (n = 3). (C) Quantification of infection based on the numbers of inclusions found in 40 visual fields at 48 hpi (n = 4). (D-G) Colocalization analysis of EBs in PI3P-positive endosomes (visualized with mCherry-2xFYVE and DAPI) in HEp-2 cells stably expressing GFP-Fip2 mutant variants at 15 min to 60 min p.i. For each time point the intracellular distribution of inclusions was assessed in 30 cells and the localization pattern was classified as follows: P, endosome in the cell periphery; N, endosomes in the perinuclear region; vA, vesicular aggregates in cell periphery. (D) Wild-type GFP-Fip2. (E) GFP-Fip2ΔC2. (F) GFP-Fip2ΔRBD. (F) GFP-Fip2ΔMyoBD. *** P value ≤0.001, ** P value ≤0.01, * P value ≤0.05, n.s. P value ≤0.01.