Fig. 1. Engineering of a Swirling Microvortex Reactor (SMR).
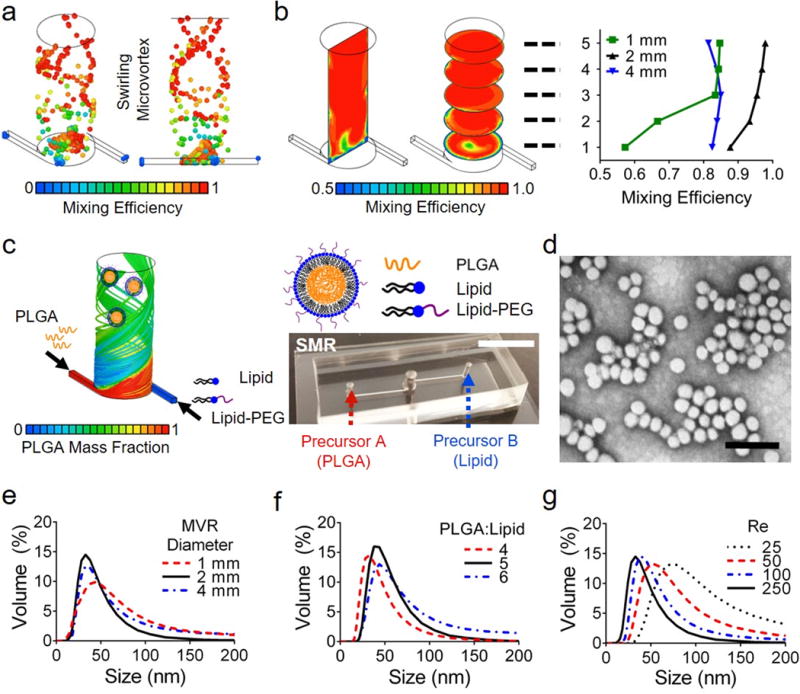
(a,b) CFD simulations of the SMR predicting the mixing efficiency (a) of virtual nanoparticles within the swirling microvortex flow and (b) at cross-sections along the height of the SMR with varied diameters (1mm, 2mm, and 4mm). (c) Schematic showing the synthesis of lipid-polymer nanoparticles (LPNPs) through swirling microvortex flow of PLGA and Lipid/Lipid-PEG aqueous solutions; Photo of a SMR with two precursor inlets. Scalebar is 5mm. (d) TEM image of synthesized LPNPs. Scalebar is 100nm. (e–g) Size distributions of synthesized LPNPs show the effects of (e) the reactor diameter, (f) PLGA-lipid weight ratio (precursor composition), and (g) Reynolds number (Re) on the average size and uniformity of the NPs.
