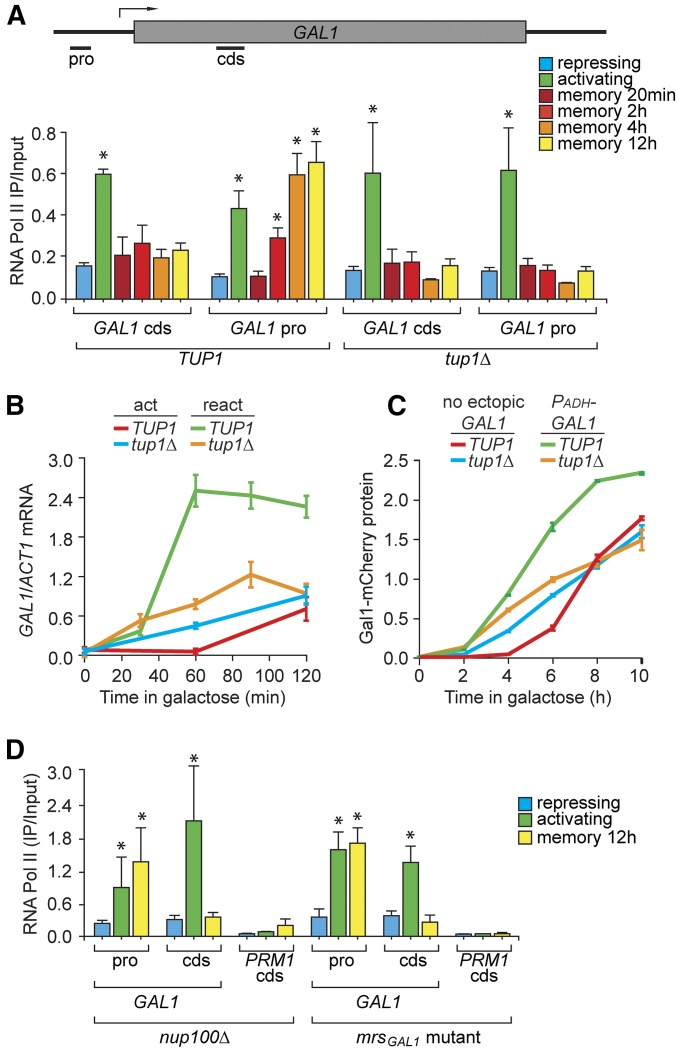
Figure 4.
Tup1 functions downstream of Gal1 to promote binding of RNAPII to the promoter and faster reactivation of GAL1 during memory. (A) RNAPII ChIP from wild-type and tup1∆ cells under repressing (glucose), activating (galactose), and at different times during memory (galactose → glucose, 20 min to 12 hr) conditions. Recovery of the GAL1 promoter and cds was quantified relative to input by qPCR. (B) Time course of RT-qPCR for GAL1 expression relative to ACT1 during activation (act; glucose → galactose) and reactivation (react; galactose → glucose 12 hr → galactose) in WT and tup1Δ cells. (C) Gal1-mCherry expression during activation in wild-type and tup1Δ cells with or without PADH-GAL1 integrated at the TRP1 locus. (D) RNAPII ChIP under repressing (glucose), activating (galactose), and memory (galactose → glucose, 12 hr) conditions for mrsGAL1 and nup100∆ mutant. Error bars represent SEM for at least three biological replicates. * P ≤ 0.05 (Student’s t-test) relative to the repressing condition. cds, coding sequence; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; pro, promoter; qPCR, quantitative PCR; RNAPII, RNA polymerase II; WT, wild type.