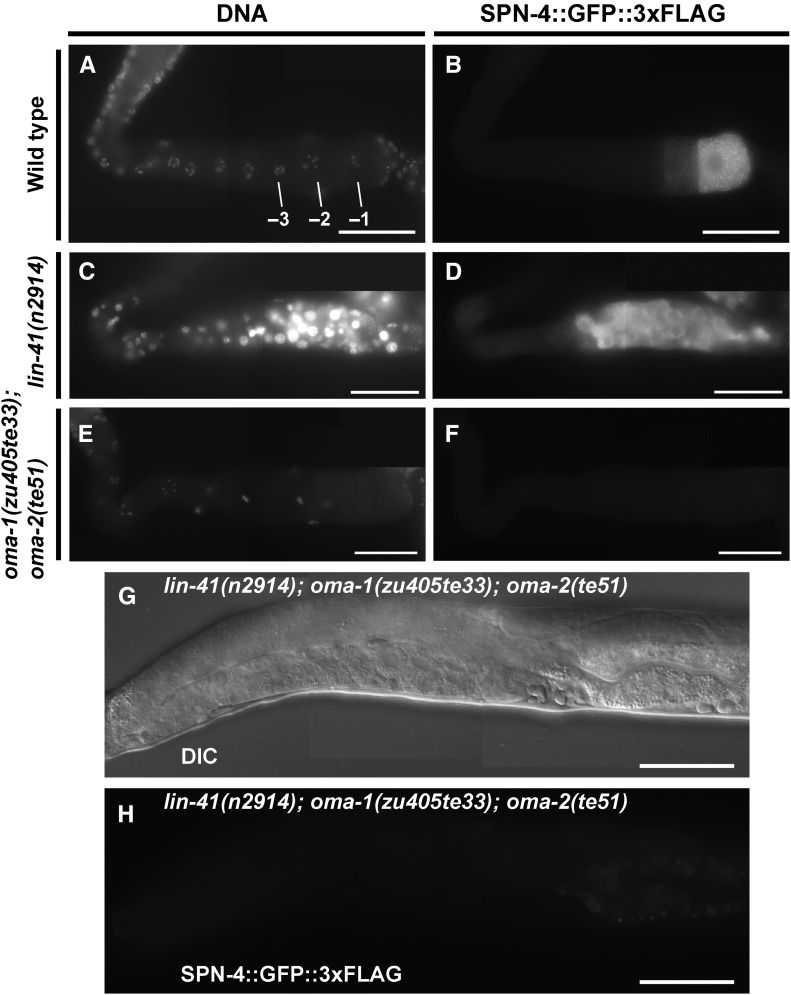
Figure 8.
LIN-41 and the OMA proteins regulate spn-4 expression in an antagonistic fashion. (A–F) The expression of spn-4 was analyzed in dissected gonads from wild type (strain DG4158), lin-41 null (from strain DG4176), and oma-1; oma-2 null (from strain DG4239) backgrounds. SPN-4::GFP::3xFLAG expression was detected by indirect immunofluorescence in dissected and fixed gonads stained with anti-FLAG antibody. DNA was detected with DAPI. (G) DIC and (H) GFP fluorescence images of a living adult hermaphrodite showing an absence of SPN-4::GFP::3xFLAG expression in proximal oocytes in a lin-41(n2914); oma-1(zu405te33); oma-2(te51) triple null mutant (from strain DG4313). SPN-4::GFP::3xFLAG expression is unaffected in the distal proliferative zone in this genetic background, but this is not shown in this image (T. Tsukamoto and D. Greenstein, unpublished results). All strains shown contain a spn-4(spn-4::gfp::3xflag) edit, which is (A–D) spn-4(tn1699) or (E–H) spn-4(tn1718). The tight linkage of spn-4 and oma-2 necessitated independent targeting of spn-4. spn-4(tn1718) and spn-4(tn1699) are the same at the DNA sequence level and exhibit identical expression patterns. oma-1(RNAi); oma-2(RNAi) prevents expression of spn-4(tn1699) (Figure S2 in File S4; n = 31). Bar, 50 μm.