Figure 1.
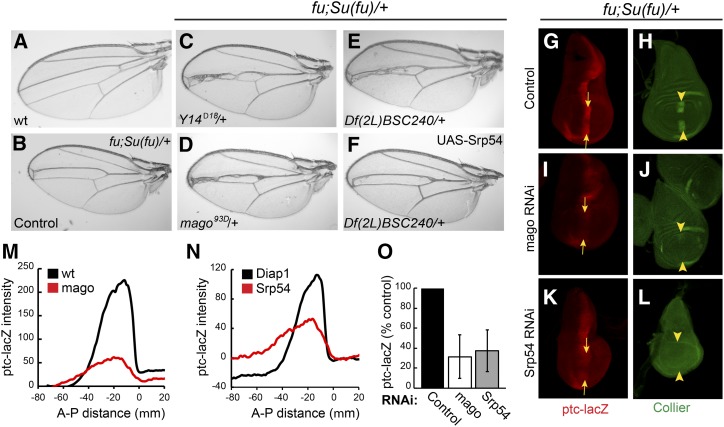
Screen for Hh pathway modifiers. (A–F) Wings from (A) wild-type males and (B–F) fu; Su(fu)/+ males. (B) Narrowing of the central veins was increased by heterozygosity for (C) Y14Δ18 and (D) mago93D. Narrowing due to (E) Df(2L) BSC240 was (F) largely suppressed by expression of UAS-Srp54 cDNA with C765-GAL4. (G and H) Wing discs from fu; Su(fu)/+ larvae have reduced expression at the AP border (yellow arrows) of (G) ptc-lacZ (red) and (H) Collier [green; restricted to the wing pouch (arrowheads)] relative to wild-type (data not shown). (I–L) Both ptc-lacZ and Collier were reduced further by C765-GAL4-driven expression of (I and J) UAS-mago RNAi or (K and L) UAS-Srp54 RNAi together with UAS-Diap1 (UAS-Diap1 was always used as a control for this genotype). Reduced ptc induction limits Ptc-induced endocytosis of Hh, so a weaker ptc-lacZ AP border stripe is also generally broader. (M and N) Average ptc-lacZ intensity along the AP axis (anterior to the left of zero) of the wing pouch for four wing discs in a single experiment, comparing (M) UAS-mago RNAi to control and (N) UAS-Srp54 RNAi to control (both also express UAS-Diap1). (O) Maximal ptc-lacZ intensity at the AP border (derived from profiles along the AP axis) as a percentage of controls for discs expressing mago and Srp54 RNAi, showing means and 95% C.I.s (n = 4 experiments for mago RNAi and n = 3 experiments for Srp54 RNAi). AP, anterior/posterior; Hh, Hedgehog; Ptc, Patched; RNAi, RNA interference; wt, wild-type.