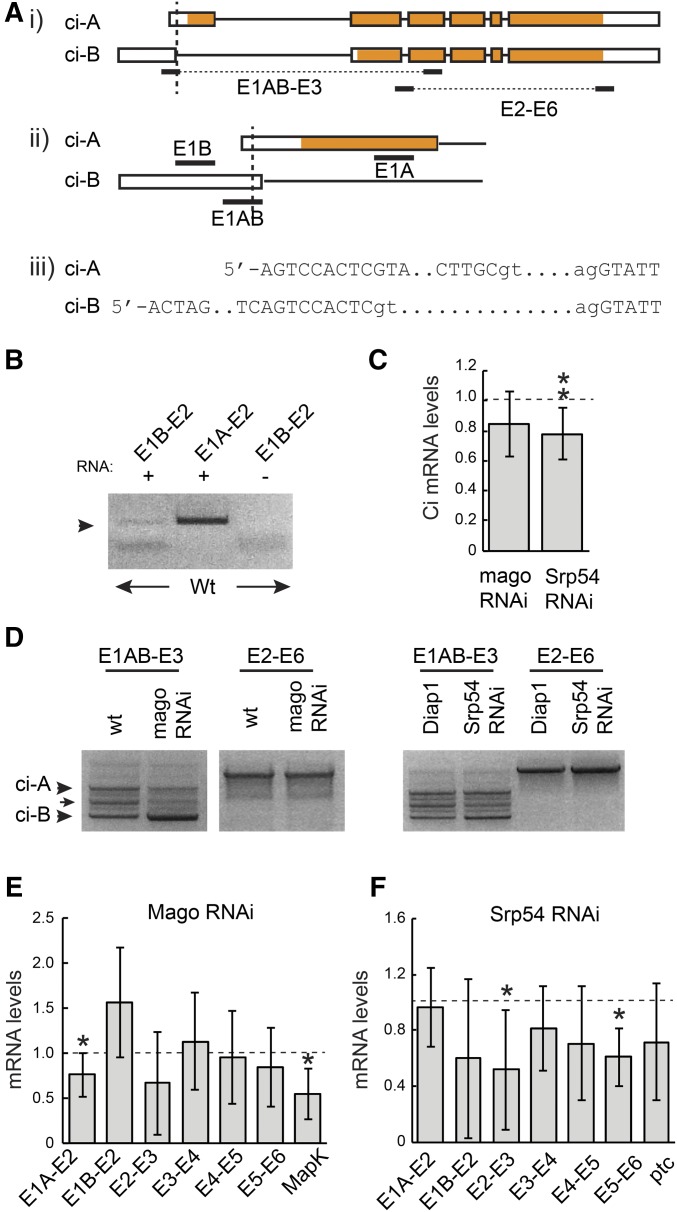
Figure 3.
Mago and Srp54 regulate ci RNA. (A) Schematic representation of ci-A and ci-B RNAs, together with primer locations (exons are boxed with translated segments in orange). The TSS of B is 742 nt upstream of TSS-A. ci-B first exon donor splice site is 8 nt downstream of TSS-A. ci-A first exon is 469 nt and first intron is 3446 nt; ci-B first exon is 751 nt and first intron is 3906 nt. (B) RT-PCR products from wild-type wing disc RNA using the indicated primer pairs. (C) ci RNA levels as a fraction of controls (set at 1.0; dashed line) measured by qRT-PCR with primers from exon 3 and spanning the exon 2/3 junction for total RNA from wing discs expressing mago RNAi or Srp54 RNAi. (D) RT-PCR products obtained using the indicated primer pairs using RNA from wing discs with reduced Mago, Srp54, or their controls. Products of the expected sizes for ci-A and ci-B (arrowheads) were confirmed by sequencing. An intermediate band (arrow) revealed a clear product on one occasion, corresponding to splicing between the ci-B donor site and an acceptor 277 nt downstream, followed by splicing in the ci-A pattern (and therefore encoding the normal Ci-A protein product). (E and F) RNA levels as a fraction of controls (set at 1.0; dashed line) measured by qRT-PCR using primers spanning each exon junction of ci and exons 6–7 of MAPK for wing discs expressing (E) UAS-mago RNAi or (F) UAS-Srp54 RNAi compared to controls. (C, E, and F) Values in all qRT-PCR experiments were first normalized to Rp49 and Rpl45 levels. Means and 95% C.I.s are shown relative to controls (set at 1.0) for (C) n = 9 experiments and (E and F) n = 3 experiments for all except E1A–E2 for mago and Srp54 RNAi (n = 7), E1B–E2, E2–E3, E4–E5, and E5–E6 for mago RNAi (n = 4), MAPK (n = 5), and E5–E6 for Srp54 RNAi (n = 4). Significant differences to controls were also calculated by Student’s t-test (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01). qRT-PCR, quantitative RT-PCR; RNAi, RNA interference; TSS, transcription start site; wt, wild-type.