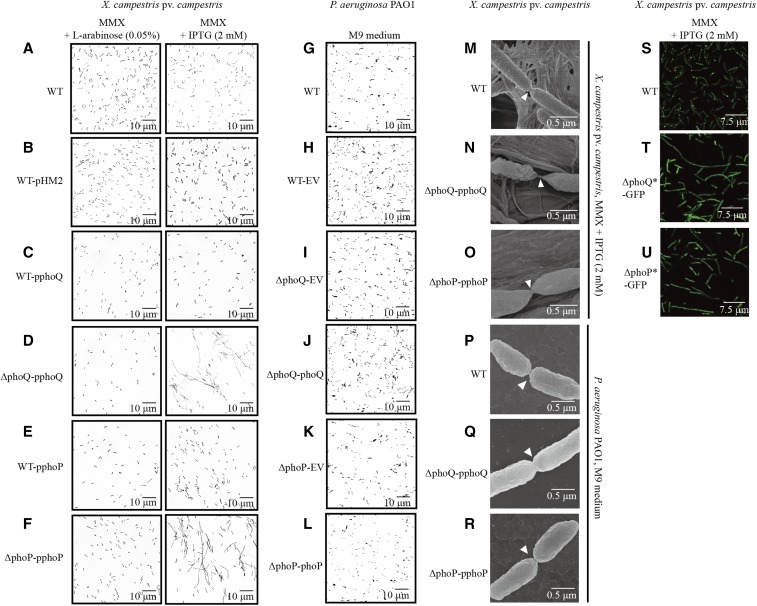
Figure 4.
Inactivation of phoPXcc and phoQXcc causes abnormalities in bacterial cell division. (A–F) Morphology of X. campestris pv. campestris cells observed under light microscopy. The bacterial strains were grown in MMX plus L-arabinose (0.05%) or MMX plus IPTG (2 mM). (G–I) Morphology of P. aeruginosa cells observed under light microscopy. The bacterial strains were grown in M9 medium. (M–O) Morphology of X. campestris pv. campestris cells observed under field emission scanning electron microscopy. The bacterial strains were grown in MMX plus IPTG (2 mM). (P–R) Morphology of P. aeruginosa cells observed under field emission scanning electron microscopy. The bacterial strains were grown in M9 medium. (S–U) Localization of FtsZ-eGFP in X. campestris pv. campestris cells. The bacterial strains were grown in MMX plus IPTG (2 mM). Scale bars are provided in the photographs. The genotypes of the bacterial strains are listed in Table S1 in File S1. eGFP, enhanced GFP; EV, empty vector; MMX, minimal medium for Xanthomonas campestris; WT, wild-type.