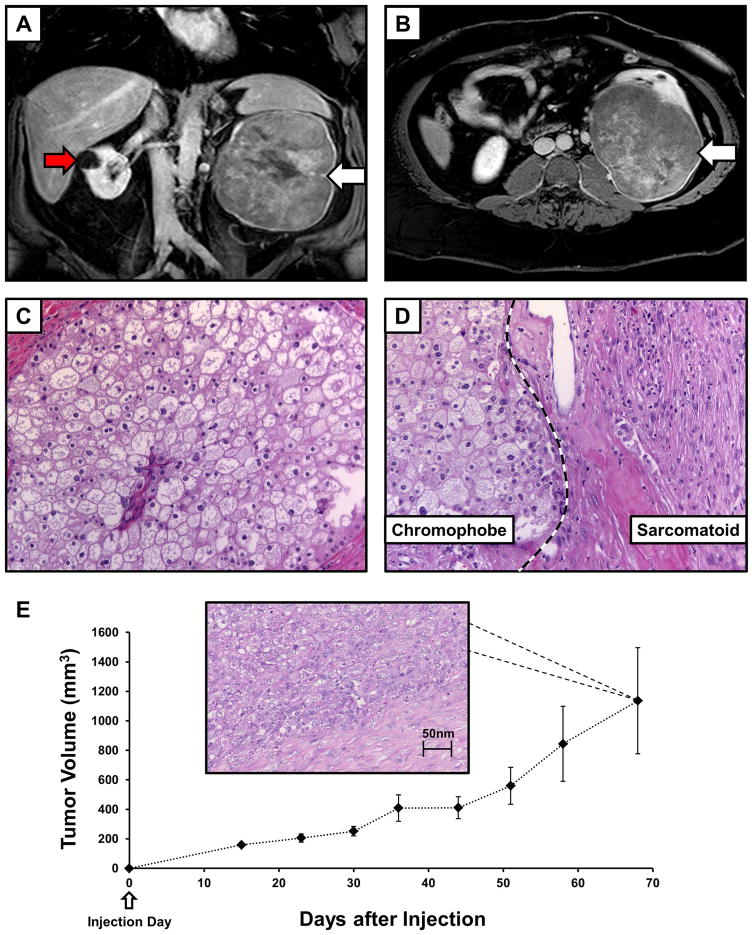
FIGURE 1.
Imaging and histology for the UOK276 cell line. (A) Contrast enhanced MRI T1 coronal imaging demonstrated the size and extent of the tumor in the left kidney (white arrow), as well as a cyst on the right kidney (red arrow). (B) Axial T1 imaging demonstrated that the tumor had almost replaced the entirety of the left kidney (white arrow). (C) Histopathology assessment of an H&E slide demonstrated large polygonal cells with irregular nuclei and well demarcated cellular borders consistent with chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (ChRCC) and (D) identified sarcomatoid areas with the large spindled, pleomorphic cells (original magnification 40x). (E) Ten athymic nude mice were each injected in the flank with ~5 million UOK276 cells resulting in the growth of measurable xenograft tumors in all mice. The xenograft tumors grew rapidly to over 1 cm diameter tumors (>500 mm3) within approximately 50 days of injection. An example of H & E staining from one of the xenograft tumors is shown that demonstrates a pathology consistent with the higher grade, sarcomatoid regions of the original chromophobe tumor.