Figure 2.
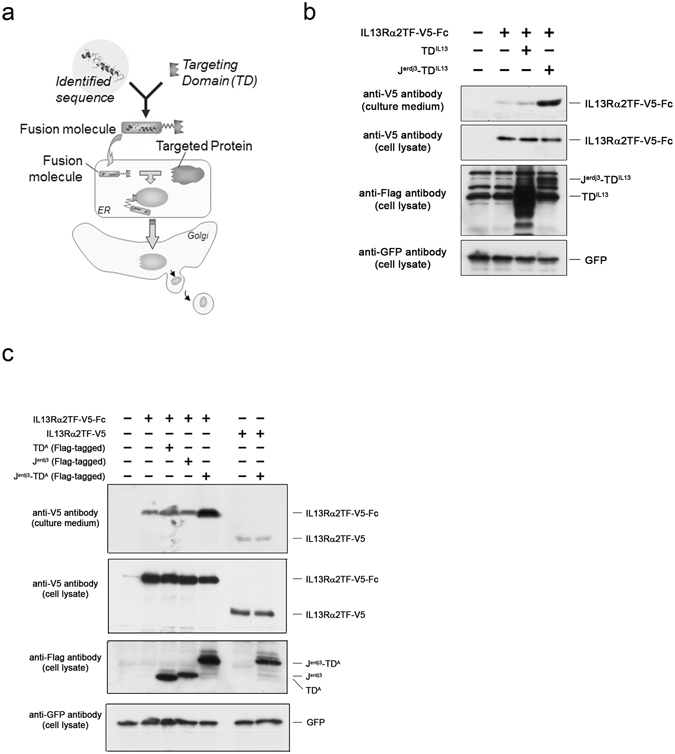
Protein expression enhanced by fusion protein with the identified J-domain sequence. (a) Depicts a diagram of a general scheme in which a fusion molecule of the J-domain fragment sequence enhances the expression of a target protein of interest. In the scheme, a J-domain fusion protein comprises a J-domain fragment sequence linked to a target protein-binding domain, wherein the target-binding domain specifically binds to a target protein of interest and the J-domain fragment sequence modulates the protein folding/cellular quality control system. This results in the enhanced secretion of a target protein. (b) HEK293 cells were transfected to express V5-tagged IL13Rα2TF (IL13Rα2TF-V5) with (+) or without (−) a Flag-tagged J-domain fusion protein incorporating the IL13 sequence as a targeting domain (Jerdj3-TDIL13). IL13Rα2TF-Fc was also expressed with a Flag-tagged targeting domain (TDIL13). Two days later, the culture medium and cell lysates were harvested and assayed by western blot analysis, as indicated. In the absence of a J-domain fusion protein, most of IL13Rα2TF-V5 was retained inside the cells and not secreted (lane 2). The secretion of IL13Rα2TF-V5 was greatly enhanced by co-transfection with the J-domain fragment fusion protein (Jerdj3-TDIL13; lane 4), but not by the targeting domain only (TDIL13; lane 3). The control (lane 1) indicates empty vector transfection control. All transfectants were co-transfected with a reporter plasmid expressing GFP. The cell lysate membrane was subsequently probed with an anti-Flag antibody (to detect Flag-tagged proteins), and anti-GFP antibody (as a transfection control) (bottom panel). (c) Either V5-tagged Fc fusion protein with IL13Rα2TF (IL13Rα2TF-V5-Fc; lanes 2 through 5) or V5-tagged IL13Rα2TF (IL13Rα2TF-V5; lanes 6 and 7) was expressed in HEK293 cells with (+) or without (−) a Flag-tagged J-domain fusion protein incorporating protein A sequence as a targeting domain (Jerdj3-TDA; lanes 5 and 7). IL13Rα2TF-Fc was also expressed with either a targeting domain only (TDA; lane 3) or a Flag-tagged J-domain fragment sequence only (Jerdj3; lane 4). Two days later, the culture medium and cell lysates were harvested, followed by western blot analysis to detect the expressed proteins. Neither a targeting domain–only nor a J-domain fragment–only sequence improved the secretion of IL13Rα2TF-V5-Fc (lanes 3 and 4, respectively). However, the secretion of IL13Rα2TF-V5-Fc was greatly enhanced by co-transfection with the J-domain fragment fusion protein (lane 5), while the secretion of IL13Rα2TF-V5 was not affected by the J-domain fragment fusion protein, which was designed to bind to Fc fusion protein (lane 7). The control (lane 1) indicates empty vector transfection control. The plasmid-carrying GFP gene was also transfected as transfection reporter. The cell lysate membrane was subsequently probed with an anti-Flag antibody (to detect Flag-tagged proteins), and anti-GFP antibody (as a transfection control) (bottom panel).
