Figure 6.
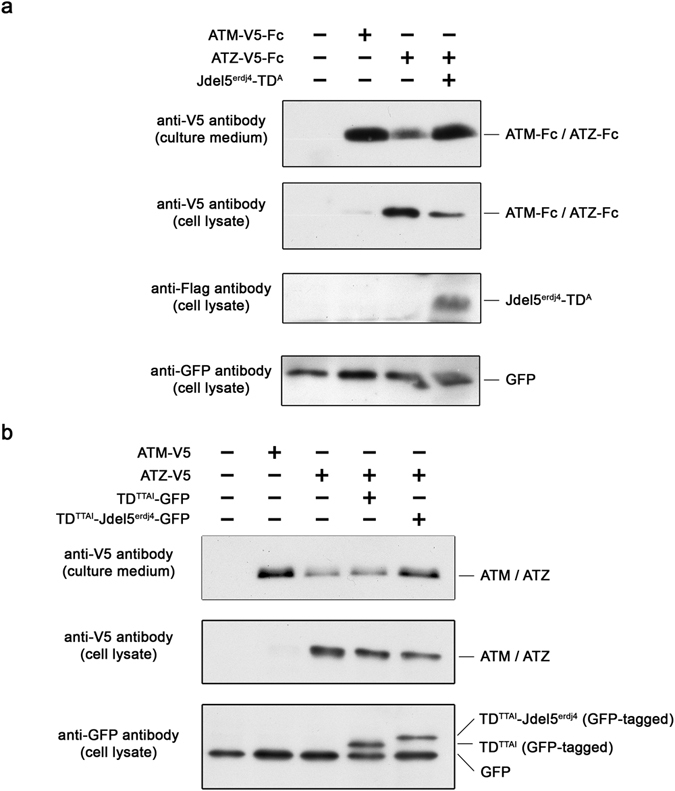
J-domain fragment fusion protein for α1 antitrypsin deficiency. (a) HEK293 cells were transfected to express Fc-fusion proteins of normal M form AT (ATM) or mutant type of AT (ATZ) with (+) or without (−) a Jdel5erdj4 fusion protein targeting Fc (Jdel5erdj4-TDA). Two days later, the cell culture medium (top panel) and cell lysate (second, third and bottom panels) were harvested, and ATM-Fc or ATZ-Fc was detected by western blot. ATM-Fc was efficiently secreted (lane 2), while ATZ-Fc was largely retained in cells (lane 3). The co-expression of the fusion protein of Jdel5erdj4 (Jdel5erdj4-TDA) significantly enhanced the secretion of ATZ-Fc and cleared ATZ-Fc from cells (lane 4). The control (left lane) indicates no transfection control. The cell lysate membrane was subsequently probed with an anti-GFP antibody as a transfection control (bottom panel). (b) Jdel5erdj4 sequence was conjugated to ATZ binding-tetrapeptide (TTAI). Tetrapeptide sequence without Jdel5erdj4 was used as a control. In order to ensure the expression of the small polypeptide, these polypeptide sequences were expressed as GFP fusion proteins (TTAI- Jdel5erdj4-GFP and TTAI-GFP). V5-tagged mutant type of AT (ATZ) was expressed with these polypeptide fusion proteins in HEK293 cells, and expressed ATZ and polypeptide fusion proteins were detected using an anti-V5 antibody or anti-GFP antibody, respectively. GFP without any polypeptide sequence was also expressed to monitor transfection efficiency.
