Figure 4.
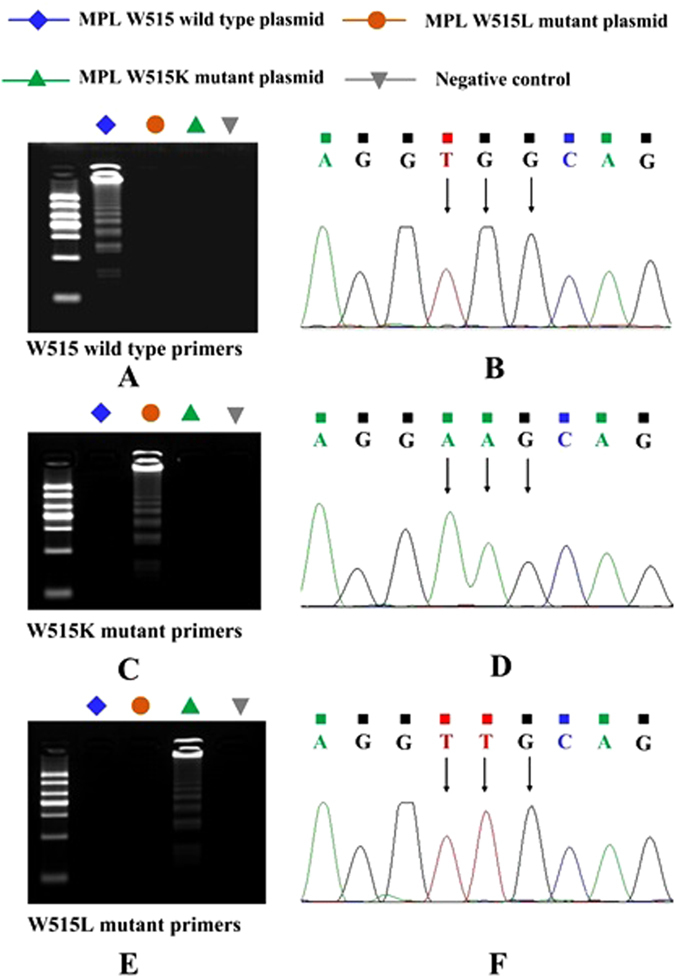
Accuracy of microchip-based LAMP for detection of the MPL W515K/L mutation. (A) Agarose gel electrophoresis of the microchip-based LAMP-amplified products with the MPL W515 wild-type primer. MPL W515 wild-type plasmid (blue), MPL W515K mutant plasmid (orange), MPL W515L mutant plasmid (green), and negative control (gray). (B) Sequencing results of the LAMP-amplified products from A. The arrowheads indicate the location of the point mutations. The wild-type sequence is TGG at this location (MPL W515 wild-type plasmid). (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis of the microchip-based LAMP-amplified products from the MPL W515K mutant primer. MPL W515 wild-type plasmid (blue), MPL W515K mutant plasmid (orange), MPL W515L mutant plasmid (green), and negative control (gray). (D) Sequencing results of the LAMP-amplified products from C. The arrowheads indicate the location of the point mutation. The mutated sequence is AAG at this location (MPL W515L plasmid). (E) Agarose gel electrophoresis of the microchip-based LAMP-amplified products with the MPL W515L mutant primer. MPL W515 wild-type plasmid (blue), MPL W515K mutant plasmid (orange), MPL W515L mutant plasmid (green), and negative control (gray). (F) Sequencing results of the LAMP-amplified products from E. The arrowheads indicate the location of the point mutation. The mutated sequence is TTG at this location (MPL W515L plasmid).
