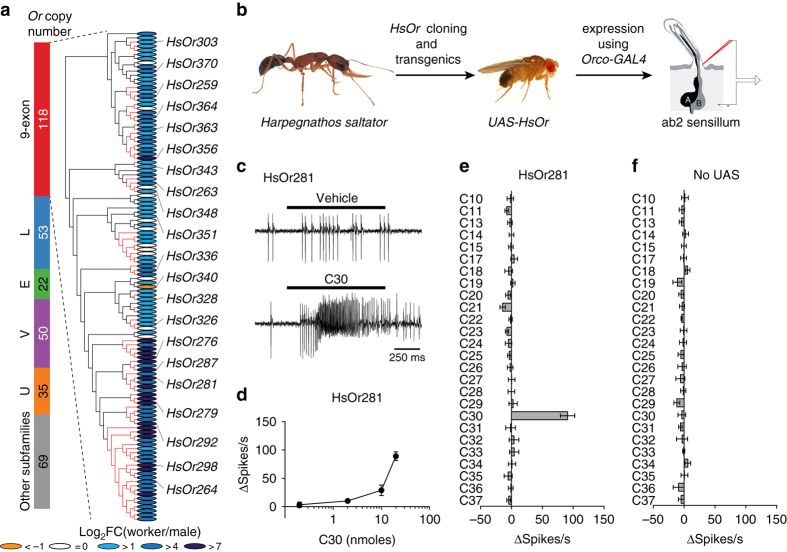
Fig. 1.
Functional identification of HsOrs that act as receptors for cuticular hydrocarbons. a Phylogeny of the nine-exon subfamily of HsOrs (left) and the HsOrs cloned and characterized in this study (right). H. saltator specific branches are in red and coloured ovals indicate the relative enrichment in worker to male comparisons for each nine-exon HsOr. b Schematic for functional characterization of HsOrs in D. melanogaster. c Representative traces of recordings from an ab2 sensillum of a w +, UAS-HsOr281; w +, Orco-GAL4 fly in response to the heated control cartridge (pentane solvent only, top) and 20 nmol of triacontane (C30, bottom). d Dose-dependent responses from HsOr281-expressing neurons to different doses of C30 (n = 5). e, f Responses of the ab2A neuron in w +, UAS-HsOr281; w + , Orco-GAL4 flies e and +; w + , Orco-GAL4 flies f to a hydrocarbon panel. All compounds were applied at 20 nmol and each value represents mean ± SEM (n = 6)