Figure 5.
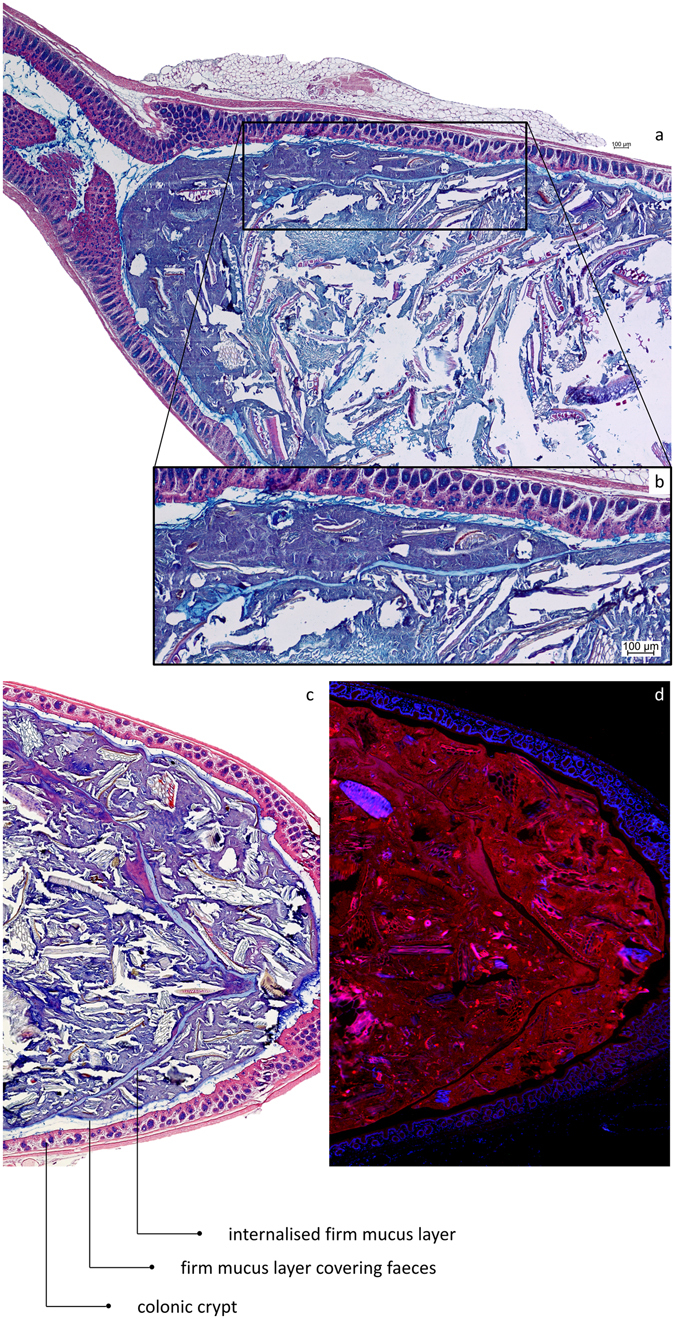
After collisions between faecal pellets in the distal colon, the mucus layers covering their surface can be internalised into the resulting composite pellet. (a) AB/H/E stained longitudinal section of distal mouse colon. (b) Close-up showing the internalised firm mucus layer. (c) AB/H/E stained longitudinal section of distal mouse colon. A firm mucus layer devoid of bacteria is found inside the pellet. (d) FISH stained (Bacteria in red; nuclei in blue) longitudinal section of mouse distal colon, the internalised firm mucus layer is recognised by the absence of bacteria.
