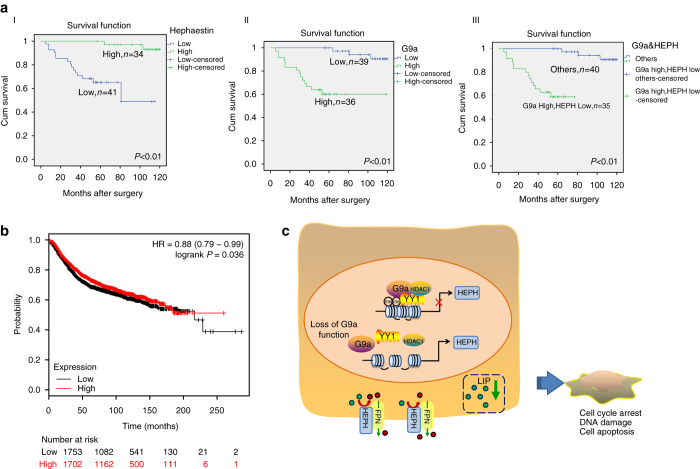
Fig. 7.
High levels of G9a and low levels of HEPH correlate with poor survival in breast cancer. a G9a and HEPH prognostic interactions. Associations between OS and high or low G9a and HEPH expression levels (based on mean partitioning) in a combined multi-institutional population-based cohort consisting of 75 breast cancer cases. Kaplan–Meier plots and log-rank P-values are shown for (I) HEPH expression, (II) G9a expression, (III) high G9a dichotomized by low HEPH. b Public breast cancer database (KM-Plotter) was queried to examine the association between patients with breast cancer RFS and HEPH expression, the log-rank test P-value was indicated. c Schematic diagram depicting the regulation of HEPH in breast tumor cells. G9a as an HMTase activity-dependent repressor collaborates in the complex with YY1 and HDAC1, and works coordinately to contribute to the reduction of HEPH expression. Silencing of G9a upregulates HEPH, inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation and cell survival via upregulation of HEPH transcription and induces HEPH-mediated iron homeostasis disruption upon greater iron export. Green particles represent ferrous iron; red particles represent ferric iron